Diabetes diets focus on managing blood sugar levels through mindful food choices, and at larosafoods.com, we understand the importance of this. Our comprehensive resources provide delicious recipes and clear guidance for creating balanced meals. By understanding the glycemic index and incorporating portion control strategies, you can navigate a diabetic food chart effectively. Let larosafoods.com be your guide to mastering diabetes management through diet and nutrition.
1. Understanding Diabetes Diets: What You Need to Know
Are diabetes diets simply about restricting what you eat, or is there more to it?
Diabetes diets are not about deprivation but rather about making informed food choices that help manage blood sugar levels effectively. According to the American Diabetes Association, a diabetes diet is a healthy eating plan that is naturally rich in nutrients and low in fat and calories. This involves focusing on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while limiting added sugars, processed foods, and unhealthy fats. A well-structured diabetes diet can help maintain healthy blood glucose levels, manage weight, and reduce the risk of diabetes complications.
1.1. The Primary Goals of Diabetes Diets
What are the main objectives of following a diabetes diet?
The primary goals include maintaining stable blood sugar levels, managing weight, and preventing diabetes complications. Diabetes diets aim to keep blood glucose levels within a target range by balancing carbohydrate intake with insulin or other medications. Weight management is crucial because obesity can worsen insulin resistance. Preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage is achieved through healthy food choices that reduce risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol.
1.2. Tailoring Your Diet to Your Needs
How do you customize a diabetes diet to fit your individual needs and preferences?
Customizing a diabetes diet involves working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that considers your health status, medication regimen, activity level, and personal preferences. According to a study by the University of California, San Francisco, individualizing diabetes diets based on cultural preferences and lifestyle can lead to better adherence and outcomes. This tailored approach ensures that the diet is sustainable and enjoyable, making it easier to manage diabetes in the long term. At larosafoods.com, we provide a variety of recipes and resources that can be adapted to individual tastes and dietary needs.
2. The Importance of a Diabetic Food Chart
Why is a diabetic food chart such a valuable tool in managing diabetes?
A diabetic food chart is essential because it provides a clear, organized overview of foods that are safe and beneficial for people with diabetes. It helps individuals understand the carbohydrate content, glycemic index (GI), and portion sizes of different foods, enabling them to make informed choices and manage their blood sugar levels effectively. According to the American Diabetes Association, using a diabetic food chart can simplify meal planning and promote better adherence to dietary guidelines.
2.1. Key Components of a Diabetic Food Chart
What information should a comprehensive diabetic food chart include?
A comprehensive diabetic food chart should include:
- Food Name: Lists various food items.
- Serving Size: Specifies the appropriate portion for each food.
- Carbohydrate Content: Indicates the amount of carbohydrates per serving.
- Glycemic Index (GI): Classifies foods based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels.
- Fiber Content: Shows the amount of fiber, which can help slow down glucose absorption.
- Nutrient Information: Includes details on fats, proteins, and calories.
2.2. Benefits of Using a Diabetic Food Chart
How does using a diabetic food chart improve diabetes management?
Using a diabetic food chart offers several benefits:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Helps in selecting foods that have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
- Enhanced Meal Planning: Simplifies the process of creating balanced, diabetes-friendly meals.
- Portion Control: Guides proper serving sizes to prevent overeating.
- Dietary Variety: Encourages the inclusion of a wide range of healthy foods.
- Increased Awareness: Educates individuals about the nutritional content of foods.
- Better Weight Management: Supports weight loss or maintenance through informed food choices.
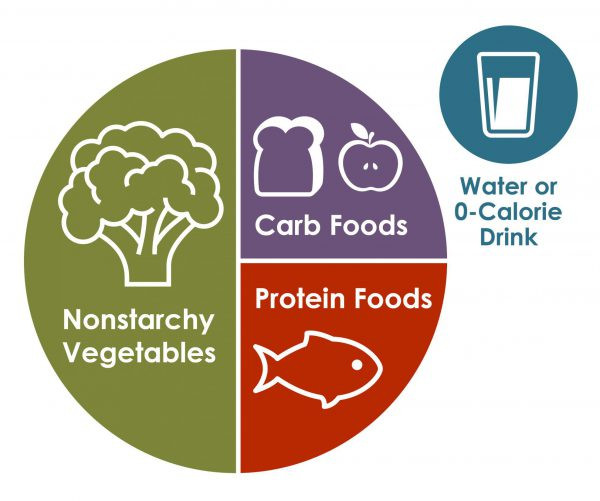
3. Foods to Include in Your Diabetes Diet
What types of foods are recommended for a diabetes-friendly diet?
A diabetes-friendly diet should include non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and healthy fats to support stable blood sugar levels and overall health. According to Diabetes UK, a balanced diet that incorporates these food groups can help manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
3.1. Non-Starchy Vegetables: The Foundation of Your Diet
Why are non-starchy vegetables so important in a diabetes diet?
Non-starchy vegetables are low in carbohydrates and calories but high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an essential part of a diabetes diet. These vegetables help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down glucose absorption and promoting satiety, which aids in weight management. Medical News Today emphasizes that incorporating a variety of non-starchy vegetables into your daily meals can significantly improve overall health and reduce the risk of diabetes complications.
Examples of non-starchy vegetables include:
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Green beans
- Asparagus
- Bell peppers
- Cucumbers
- Lettuce
- Zucchini
- Brussels sprouts
3.2. Lean Proteins: Essential for Muscle Health
How does lean protein benefit individuals with diabetes?
Lean protein is essential for muscle health and provides a steady source of energy without causing significant spikes in blood sugar levels. Protein helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes satiety, and supports weight management, making it a crucial component of a diabetes diet. According to Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, incorporating lean protein sources into meals can help stabilize blood glucose and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Good sources of lean protein include:
- Chicken breast (skinless)
- Turkey breast
- Fish (salmon, tuna, cod)
- Tofu
- Beans and legumes
- Eggs
- Low-fat dairy products
3.3. Whole Grains: A Better Carbohydrate Choice
Why are whole grains preferred over refined grains in a diabetes diet?
Whole grains are preferred because they are high in fiber, which slows down the absorption of glucose and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Unlike refined grains, whole grains retain their bran and germ, providing essential nutrients and promoting satiety. The Mayo Clinic recommends choosing whole grains over refined grains to improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes complications.
Examples of whole grains include:
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Whole wheat bread
- Barley
- Whole grain pasta
3.4. Fruits: Enjoy in Moderation
How can fruits be included in a diabetes diet without causing blood sugar spikes?
Fruits can be included in a diabetes diet in moderation by choosing low-glycemic fruits and pairing them with protein or healthy fats to slow down glucose absorption. Portion control is also essential to prevent blood sugar spikes. The American Diabetes Association suggests that fruits are a healthy part of a diabetes diet when consumed in appropriate amounts.
Examples of diabetes-friendly fruits include:
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
- Apples
- Pears
- Cherries
- Peaches
- Oranges
- Grapefruit
3.5. Healthy Fats: Support Overall Health
Why are healthy fats important for individuals with diabetes?
Healthy fats are important for overall health as they support heart health, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity. Incorporating healthy fats into a diabetes diet can help manage cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. The American Heart Association recommends including sources of healthy fats in your daily meals to support overall well-being.
Sources of healthy fats include:
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds
- Olive oil
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
4. Foods to Avoid or Limit in Your Diabetes Diet
What foods should individuals with diabetes avoid or limit to manage their blood sugar effectively?
Individuals with diabetes should avoid or limit sugary drinks, processed foods, refined grains, and high-fat foods to manage their blood sugar effectively. These foods can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose levels and contribute to weight gain, increasing the risk of diabetes complications. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), minimizing these foods can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
4.1. Sugary Drinks: The Culprit Behind Blood Sugar Spikes
Why are sugary drinks harmful for people with diabetes?
Sugary drinks such as sodas, fruit juices, and sweetened beverages are harmful because they contain high amounts of added sugars, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. These drinks provide empty calories without any nutritional value and can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting the intake of sugary drinks to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and other health complications.
Examples of sugary drinks to avoid include:
- Sodas
- Fruit juices with added sugar
- Sweetened teas
- Energy drinks
- Sweetened coffee drinks
- Sports drinks
4.2. Processed Foods: High in Unhealthy Additives
How do processed foods affect blood sugar and overall health in people with diabetes?
Processed foods are often high in unhealthy additives, such as added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can negatively affect blood sugar and overall health in people with diabetes. These foods are typically low in fiber and essential nutrients, leading to rapid glucose absorption and increased risk of chronic diseases. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that a diet high in processed foods is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Examples of processed foods to limit include:
- Fast food
- Packaged snacks (chips, cookies, candies)
- Processed meats (sausage, bacon, deli meats)
- Frozen meals
- Canned soups
4.3. Refined Grains: Lacking Essential Nutrients
Why should refined grains be limited in a diabetes diet?
Refined grains, such as white bread, white rice, and pastries, should be limited because they are low in fiber and nutrients, causing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. These grains have been stripped of their bran and germ, removing essential vitamins and minerals that are beneficial for health. The American Diabetes Association recommends choosing whole grains over refined grains to improve blood sugar control and overall health.
Examples of refined grains to limit include:
- White bread
- White rice
- Pastries
- Cereals
- Pasta
4.4. High-Fat Foods: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity
How do high-fat foods affect insulin sensitivity and overall diabetes management?
High-fat foods, especially those high in saturated and trans fats, can negatively impact insulin sensitivity and overall diabetes management. These fats can contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, making it harder to control blood sugar levels. The American Heart Association advises limiting saturated and trans fats and choosing healthier fats like unsaturated fats to support heart health and improve insulin sensitivity.
Examples of high-fat foods to limit include:
- Fried foods
- Fatty cuts of meat
- Full-fat dairy products
- Processed snacks (chips, pastries)
5. Sample Meal Plans for Diabetes
What does a well-structured, diabetes-friendly meal plan look like?
A well-structured, diabetes-friendly meal plan includes balanced portions of non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and healthy fats to ensure stable blood sugar levels and overall nutritional balance. According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, a sample meal plan should be individualized based on personal preferences, dietary needs, and medication regimen.
5.1. Sample Meal Plan: Breakfast
What are some diabetes-friendly breakfast options?
- Oatmeal with Berries and Nuts:
- 1/2 cup cooked oatmeal
- 1/4 cup mixed berries
- 1 tablespoon chopped nuts
- Greek Yogurt with Fruit and Seeds:
- 1 cup plain Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup sliced peaches
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- Whole Grain Toast with Avocado and Egg:
- 1 slice whole grain toast
- 1/4 avocado, sliced
- 1 poached egg
5.2. Sample Meal Plan: Lunch
What are some diabetes-friendly lunch options?
- Grilled Chicken Salad:
- 3 ounces grilled chicken breast
- 2 cups mixed greens
- 1/2 cup non-starchy vegetables (cucumber, bell peppers, tomatoes)
- 2 tablespoons vinaigrette dressing
- Turkey and Avocado Wrap:
- Whole grain tortilla
- 3 ounces sliced turkey breast
- 1/4 avocado, mashed
- Lettuce and tomato
- Lentil Soup with Whole Grain Bread:
- 1 1/2 cups lentil soup
- 1 slice whole grain bread
5.3. Sample Meal Plan: Dinner
What are some diabetes-friendly dinner options?
- Baked Salmon with Roasted Vegetables:
- 4 ounces baked salmon
- 1 cup roasted vegetables (broccoli, carrots, Brussels sprouts)
- 1/2 cup quinoa
- Chicken Stir-Fry:
- 3 ounces diced chicken breast
- 1 1/2 cups stir-fried vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas)
- 1/2 cup brown rice
- Black Bean Burgers on Whole Grain Buns:
- 1 black bean burger
- Whole grain bun
- Lettuce, tomato, and avocado
5.4. Sample Meal Plan: Snacks
What are some healthy snack options for people with diabetes?
- Apple Slices with Peanut Butter:
- 1 medium apple, sliced
- 2 tablespoons peanut butter
- Handful of Almonds:
- 1/4 cup almonds
- Carrot Sticks with Hummus:
- 1 cup carrot sticks
- 2 tablespoons hummus
- Greek Yogurt with Berries:
- 1 cup plain Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup mixed berries
6. Practical Tips for Following a Diabetes Diet
What are some practical strategies to help people stick to their diabetes diet?
Practical strategies include meal planning, portion control, reading food labels, staying hydrated, and seeking support from healthcare professionals. These tips can help individuals manage their blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy lifestyle. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), incorporating these strategies can lead to better diabetes management and overall health outcomes.
6.1. Meal Planning: Stay on Track
How can meal planning help manage diabetes?
Meal planning helps manage diabetes by ensuring balanced meals, consistent carbohydrate intake, and portion control, all of which are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Planning meals in advance reduces the likelihood of impulsive, unhealthy food choices and promotes better dietary adherence. At larosafoods.com, you can find a wealth of recipes and meal planning guides tailored to diabetes-friendly eating.
6.2. Portion Control: Avoid Overeating
Why is portion control important for people with diabetes?
Portion control is crucial because it helps prevent overeating, which can lead to blood sugar spikes and weight gain. By understanding appropriate serving sizes and using tools like measuring cups and food scales, individuals with diabetes can better manage their carbohydrate intake and maintain stable blood glucose levels. The American Diabetes Association emphasizes that portion control is a key component of a successful diabetes diet.
6.3. Reading Food Labels: Make Informed Choices
How can reading food labels help people make better dietary choices?
Reading food labels helps people make informed dietary choices by providing essential information about the carbohydrate content, serving sizes, and ingredients in packaged foods. By carefully reviewing food labels, individuals with diabetes can identify hidden sugars, unhealthy fats, and high sodium levels, enabling them to select healthier options that support blood sugar control. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides resources and guidelines for understanding food labels and making informed decisions.
6.4. Stay Hydrated: Drink Plenty of Water
Why is staying hydrated important for managing diabetes?
Staying hydrated is crucial for managing diabetes because water helps regulate blood sugar levels, supports kidney function, and promotes overall health. Dehydration can lead to increased blood sugar concentrations and reduced insulin sensitivity. The Mayo Clinic recommends drinking plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support optimal diabetes management.
6.5. Seek Support: Healthcare Professionals
How can healthcare professionals help individuals with diabetes manage their diet?
Healthcare professionals, such as doctors, registered dietitians, and diabetes educators, can provide personalized guidance, education, and support to help individuals with diabetes manage their diet effectively. They can create tailored meal plans, offer advice on portion control and food choices, and provide ongoing support to address any challenges or concerns. The American Association of Diabetes Educators (AADE) offers resources and tools for finding qualified healthcare professionals who specialize in diabetes management.
7. Common Myths About Diabetes Diets
What are some common misconceptions about diabetes diets?
Common myths include the beliefs that people with diabetes cannot eat any sweets, must follow a restrictive diet, and only need to focus on sugar intake. These misconceptions can lead to unnecessary dietary restrictions and confusion about proper diabetes management. According to experts at the University of California, Berkeley, dispelling these myths can help individuals with diabetes adopt a balanced and sustainable eating plan.
7.1. Myth 1: People With Diabetes Cannot Eat Any Sweets
Can people with diabetes ever enjoy sweets?
People with diabetes can enjoy sweets in moderation as part of a balanced diet. The key is to control portion sizes and choose healthier options, such as fruits or sugar-free desserts. The American Diabetes Association advises that incorporating small amounts of sweets into a meal plan is possible if it fits within the overall carbohydrate goals and is balanced with other nutritious foods.
7.2. Myth 2: Diabetes Diets Are Restrictive and Unenjoyable
Are diabetes diets necessarily restrictive and unenjoyable?
Diabetes diets do not have to be restrictive or unenjoyable. By focusing on whole, nutrient-rich foods and incorporating personal preferences, individuals with diabetes can create satisfying and sustainable meal plans. At larosafoods.com, we offer a variety of delicious and diabetes-friendly recipes that prove healthy eating can be both enjoyable and manageable.
7.3. Myth 3: Only Sugar Intake Matters for Diabetes Management
Is managing diabetes solely about controlling sugar intake?
Managing diabetes involves more than just controlling sugar intake. While limiting added sugars is important, it is also crucial to balance carbohydrate intake, choose healthy fats, and consume adequate protein and fiber. Overall dietary patterns and lifestyle factors play a significant role in blood sugar control and overall health. A study published in the journal Diabetes Care emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive approach to diabetes management that includes dietary modifications, physical activity, and medication (if prescribed).
8. The Glycemic Index and Diabetes
How does the glycemic index help in managing diabetes?
The glycemic index (GI) helps manage diabetes by ranking foods based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to make informed choices about which carbohydrates to consume. Low-GI foods cause a slower and more gradual increase in blood sugar, which is beneficial for maintaining stable glucose levels. The Harvard Medical School recommends using the GI as a tool for selecting diabetes-friendly foods and managing blood sugar effectively.
8.1. Understanding the Glycemic Index (GI)
What does the glycemic index measure, and how is it classified?
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels compared to pure glucose, which has a GI of 100. Foods are classified as low, medium, or high GI:
- Low GI: 55 or less
- Medium GI: 56-69
- High GI: 70 or more
8.2. How to Use the GI in Meal Planning
How can individuals with diabetes use the glycemic index to plan their meals?
Individuals with diabetes can use the glycemic index to plan their meals by choosing more low-GI foods, which cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Pairing high-GI foods with protein or healthy fats can also help slow down glucose absorption. The American Diabetes Association suggests incorporating the GI into meal planning as part of a comprehensive approach to diabetes management.
9. Staying Motivated on Your Diabetes Diet
How can you maintain motivation and stay consistent with your diabetes diet?
Maintaining motivation involves setting realistic goals, tracking progress, finding support, and celebrating successes to foster a positive relationship with healthy eating. According to a study by Stanford University, incorporating these strategies can improve adherence to a diabetes diet and promote long-term success.
9.1. Set Realistic Goals
Why is it important to set achievable dietary goals?
Setting realistic goals is important because it promotes a sense of accomplishment and motivation, making it easier to stick to your diabetes diet in the long term. Unrealistic goals can lead to frustration and discouragement, undermining your efforts. The American Diabetes Association recommends working with a healthcare professional to set achievable dietary goals that align with your health status and lifestyle.
9.2. Track Your Progress
How can tracking your food intake and blood sugar levels help you stay motivated?
Tracking your food intake and blood sugar levels provides valuable insights into how different foods affect your glucose levels, helping you make informed dietary choices and stay motivated. Monitoring your progress can also highlight improvements and reinforce positive behaviors, encouraging you to continue on your path to better health. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers resources and tools for tracking your food intake and blood sugar levels effectively.
9.3. Find Support
Why is having a support system important for people with diabetes?
Having a support system, including family, friends, or a diabetes support group, provides encouragement, accountability, and emotional support, which can help you stay motivated and overcome challenges. Sharing your experiences with others who understand can also reduce feelings of isolation and promote a sense of community. The American Diabetes Association offers resources and support groups for people with diabetes and their families.
9.4. Celebrate Successes
Why is it important to acknowledge and celebrate your achievements?
Celebrating successes, no matter how small, reinforces positive behaviors and promotes a sense of accomplishment, helping you stay motivated and committed to your diabetes diet. Acknowledging your achievements can also boost your self-esteem and create a positive feedback loop, encouraging you to continue making healthy choices. The Joslin Diabetes Center recommends recognizing and celebrating your progress as a key strategy for long-term diabetes management.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetes Diets
Have questions about diabetes diets? Let’s address some of the most common queries to help you navigate your nutritional journey.
10.1. Can I eat carbohydrates if I have diabetes?
Yes, you can eat carbohydrates if you have diabetes. The key is to choose complex carbohydrates over simple carbohydrates, control portion sizes, and balance your carbohydrate intake with protein and healthy fats.
10.2. Are there any specific foods I should completely avoid if I have diabetes?
While you don’t necessarily need to completely avoid any specific foods, it’s best to limit sugary drinks, processed foods, and refined grains, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
10.3. How often should I eat meals and snacks when following a diabetes diet?
Eating regular meals and snacks at consistent times throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent extreme highs and lows. Aim for three meals and one to two snacks per day, depending on your individual needs and medication regimen.
10.4. Can I drink alcohol if I have diabetes?
If you have diabetes, you can drink alcohol in moderation, but it’s essential to do so safely. Always eat food when consuming alcohol, and monitor your blood sugar levels closely, as alcohol can sometimes cause hypoglycemia.
10.5. How can I handle eating out while following a diabetes diet?
When eating out, plan ahead by reviewing the menu online, choose healthier options such as lean proteins and non-starchy vegetables, and be mindful of portion sizes. Don’t hesitate to ask for modifications, such as having sauces on the side or substituting fries with a salad.
10.6. Are artificial sweeteners safe for people with diabetes?
Artificial sweeteners can be a safe alternative to sugar for people with diabetes. However, it’s essential to use them in moderation and be aware of any potential side effects.
10.7. How important is exercise in managing diabetes?
Exercise is very important in managing diabetes. Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and promote overall health.
10.8. Can stress affect my blood sugar levels?
Yes, stress can affect your blood sugar levels. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can cause your blood sugar to rise. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep can help stabilize your blood sugar levels.
10.9. What should I do if my blood sugar is consistently high despite following a diabetes diet?
If your blood sugar is consistently high despite following a diabetes diet, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider. They may need to adjust your medication, review your meal plan, or recommend additional strategies for managing your diabetes.
10.10. Where can I find reliable information and support for managing diabetes?
Reliable information and support for managing diabetes can be found at larosafoods.com, through healthcare professionals such as doctors, registered dietitians, and diabetes educators, and at organizations such as the American Diabetes Association and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Ready to take control of your diabetes management through diet? Explore the wealth of resources at larosafoods.com, where you’ll find delicious recipes, practical tips, and comprehensive information to support your journey towards better health. Whether you’re looking for meal planning assistance, nutritional guidance, or innovative ways to enjoy diabetes-friendly meals, larosafoods.com is your go-to destination. Visit us today at 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States, call us at +1 (415) 987-0123, or explore our website. Start your path to a healthier, more vibrant life with larosafoods.com.