Foods High In Potassium are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being, and larosafoods.com offers a wealth of information and recipes to help you incorporate these nutrients into your daily diet. Potassium-rich foods are crucial for nerve function, muscle contractions, and maintaining healthy blood pressure, so understanding which foods to include in your diet can significantly improve your health. Explore larosafoods.com to discover delicious and easy ways to boost your potassium intake, and improve electrolyte balance and cardiovascular health.
1. Understanding Potassium and Its Importance
What makes potassium so vital for our bodies? Potassium is an essential mineral and electrolyte that plays a key role in numerous bodily functions. Let’s delve deeper into its significance.
What is Potassium?
Potassium is a mineral and an electrolyte that helps regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals. It’s crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure and supporting overall cellular function. Potassium is naturally present in many foods and is available as a dietary supplement.
Why is Potassium Important?
Potassium is essential for maintaining various bodily functions. These functions include:
- Regulating Blood Pressure: Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body, which is vital for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
- Muscle Function: It supports muscle contractions, including those of the heart, ensuring proper function.
- Nerve Function: Potassium aids in transmitting nerve signals, which is crucial for communication between the brain and body.
- Fluid Balance: It works with sodium to maintain the body’s fluid balance, which is essential for cell function.
According to a study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in March 2024, adequate potassium intake is associated with a reduced risk of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
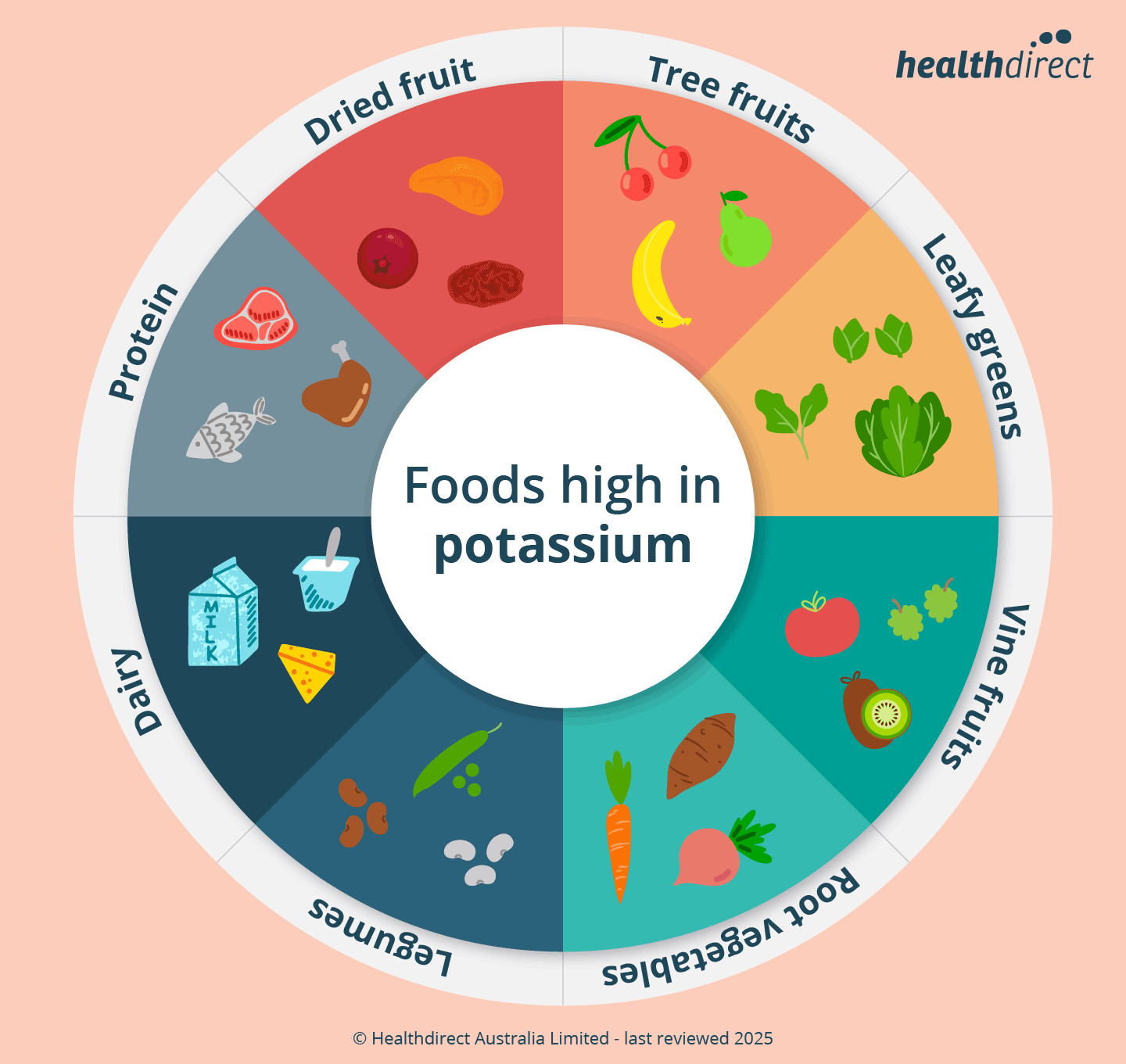
2. Top Foods High in Potassium
What are the best food sources to increase your potassium intake? Discover a variety of delicious and nutritious foods rich in potassium.
Fruits
What fruits are packed with potassium? Fruits are a delicious and convenient way to boost your potassium intake.
Bananas
Bananas are perhaps the most well-known source of potassium. A medium-sized banana contains approximately 422 mg of potassium, making it an excellent snack for a quick boost.
Avocados
Avocados are not only a healthy source of fats but also rich in potassium. One avocado contains about 690 mg of potassium.
Oranges
Oranges are a refreshing source of potassium, with one medium-sized orange providing around 237 mg. They also offer a good dose of Vitamin C.
Cantaloupe
Cantaloupe is a hydrating fruit that is also high in potassium. A cup of cantaloupe contains approximately 427 mg of potassium.
Dried Apricots
Dried apricots are a concentrated source of potassium. A half-cup serving provides about 755 mg of potassium, making them a convenient snack.
Vegetables
Which vegetables should you include in your diet for a potassium boost? Vegetables offer a wide range of nutrients, including significant amounts of potassium.
Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of potassium, with one medium-sized sweet potato containing around 542 mg. They are also rich in Vitamin A and fiber.
Potatoes
Potatoes, especially with the skin on, are high in potassium. A medium-sized potato contains about 926 mg of potassium.
Spinach
Spinach is a leafy green that provides a good amount of potassium. A cup of cooked spinach contains approximately 839 mg.
Beet Greens
Beet greens are a nutritious source of potassium. A cup of cooked beet greens contains about 1,309 mg of potassium.
White Beans
White beans are a great source of potassium and protein. A cup of cooked white beans contains approximately 1,189 mg of potassium.
Dairy and Other Sources
Are there other food groups that can help you meet your potassium needs? Dairy products and other sources can also contribute to your potassium intake.
Milk
Milk is a good source of potassium. One cup of milk contains about 350-380 mg of potassium, depending on the type of milk (whole, skim, etc.).
Yogurt
Yogurt is another excellent dairy source of potassium. A cup of plain yogurt contains approximately 400-450 mg of potassium.
Salmon
Salmon is a fatty fish that is not only rich in omega-3 fatty acids but also a good source of potassium. A 3-ounce serving contains about 414 mg of potassium.
Coconut Water
Coconut water is a natural electrolyte drink that is high in potassium. One cup contains approximately 600 mg of potassium.
Black Beans
Black beans are a versatile and nutritious source of potassium. A cup of cooked black beans contains about 739 mg of potassium.
 Foods high in potassium including white beans, coconut water, yogurt, salmon, and black beans.
Foods high in potassium including white beans, coconut water, yogurt, salmon, and black beans.
3. Benefits of Potassium-Rich Foods
How do foods high in potassium contribute to your overall well-being? Discover the health benefits of incorporating these foods into your diet.
Heart Health
Can potassium truly protect your heart? Potassium plays a vital role in maintaining heart health by regulating blood pressure and supporting proper heart muscle function.
Regulating Blood Pressure
Potassium helps balance the effects of sodium in the body, which is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. High sodium intake can lead to hypertension, while adequate potassium intake helps counteract this effect. According to the American Heart Association, increasing potassium intake while reducing sodium can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Supporting Heart Muscle Function
Potassium is essential for the proper contraction of the heart muscle. It helps maintain the electrical signals that coordinate heartbeats, ensuring that the heart pumps blood efficiently. A study published in the “Journal of the American College of Cardiology” in November 2023 found that individuals with higher potassium levels had a lower risk of heart arrhythmias and improved overall heart function.
Muscle and Nerve Function
How does potassium support your muscles and nerves? Potassium is crucial for the proper functioning of muscles and nerves, ensuring that your body can move and respond effectively.
Aiding Muscle Contractions
Potassium helps regulate muscle contractions throughout the body. It plays a key role in the transmission of electrical signals that stimulate muscle fibers to contract. This is particularly important for athletes and individuals who engage in regular physical activity. A deficiency in potassium can lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue.
Supporting Nerve Signals
Potassium is essential for the transmission of nerve signals between the brain and the body. It helps maintain the electrical potential of nerve cells, allowing them to transmit signals efficiently. This is vital for sensory perception, motor control, and cognitive function.
Bone Health
Does potassium play a role in maintaining strong bones? Emerging research suggests that potassium may contribute to bone health by neutralizing acids that can leach calcium from bones.
Neutralizing Acids
Potassium-rich foods, particularly fruits and vegetables, can help neutralize metabolic acids in the body. These acids, which are produced as a result of normal metabolic processes, can contribute to bone loss by leaching calcium from bones. By neutralizing these acids, potassium helps maintain bone density and strength.
Promoting Bone Density
Studies have shown a positive correlation between potassium intake and bone density. A meta-analysis published in the “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” in October 2022 found that individuals with higher potassium intakes had greater bone mineral density and a reduced risk of osteoporosis.
Digestive Health
How can potassium-rich foods improve your digestive system? Potassium supports healthy digestion by aiding in muscle contractions in the digestive tract and maintaining fluid balance.
Aiding Muscle Contractions in the Digestive Tract
Potassium helps regulate muscle contractions in the digestive tract, which is essential for the movement of food through the digestive system. This can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. A deficiency in potassium can lead to sluggish digestion and discomfort.
Maintaining Fluid Balance
Potassium works with sodium to maintain fluid balance in the body, which is crucial for proper digestion. Adequate hydration and electrolyte balance help keep the digestive system functioning smoothly, allowing for efficient nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
4. Potassium Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
What happens when you don’t get enough potassium? Learn about the causes and symptoms of potassium deficiency and how to prevent it.
Causes of Potassium Deficiency (Hypokalemia)
What factors can lead to low potassium levels? Potassium deficiency, also known as hypokalemia, can result from various factors.
Dietary Factors
A diet consistently low in potassium-rich foods can lead to a deficiency over time. This is more likely to occur in individuals who consume a lot of processed foods, which are often low in potassium.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of potassium deficiency. These conditions include:
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can reduce the body’s ability to regulate potassium levels.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can interfere with nutrient absorption, including potassium.
- Eating Disorders: Anorexia and bulimia can lead to electrolyte imbalances, including potassium deficiency.
Medications
Certain medications can increase potassium excretion, leading to a deficiency. These medications include:
- Diuretics (Water Pills): Often prescribed for high blood pressure, diuretics can increase potassium loss through urine.
- Laxatives: Overuse of laxatives can lead to potassium depletion.
- Certain Antibiotics: Some antibiotics can affect kidney function and increase potassium excretion.
Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency
How can you recognize if you have low potassium levels? The symptoms of potassium deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency.
Mild Symptoms
Mild potassium deficiency may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Muscle Weakness: A general feeling of weakness in the muscles.
- Muscle Cramps: Involuntary muscle contractions, often in the legs.
Severe Symptoms
Severe potassium deficiency can lead to more serious symptoms, including:
- Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia): Potassium is essential for maintaining a regular heartbeat.
- Muscle Paralysis: Inability to move muscles, which can be life-threatening.
- Difficulty Breathing: Weakness of the respiratory muscles can make breathing difficult.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Preventing Potassium Deficiency
What steps can you take to avoid potassium deficiency? Preventing potassium deficiency involves making informed dietary choices and managing any underlying medical conditions.
Dietary Recommendations
The best way to prevent potassium deficiency is to consume a balanced diet rich in potassium-rich foods. Aim to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and other sources of potassium in your daily meals.
Monitoring Medications
If you are taking medications that can affect potassium levels, work with your healthcare provider to monitor your potassium levels regularly. They may adjust your medication dosage or recommend potassium supplements to help maintain healthy levels.
Managing Medical Conditions
If you have a medical condition that increases your risk of potassium deficiency, work with your healthcare provider to manage your condition effectively. This may involve dietary changes, medication adjustments, or other interventions to help maintain healthy potassium levels.
5. Incorporating Potassium-Rich Foods into Your Diet
How can you easily add more potassium to your meals? Discover practical tips and delicious recipes to boost your potassium intake.
Breakfast Ideas
What are some potassium-packed breakfast options? Start your day off right with a potassium-rich breakfast.
Banana Oatmeal
Add sliced bananas to your morning oatmeal for a boost of potassium and fiber. You can also sprinkle some dried apricots on top for extra potassium.
Yogurt with Berries
Enjoy a cup of plain yogurt with a mix of berries, such as strawberries and blueberries. Yogurt is a good source of potassium, and berries add antioxidants and flavor.
Smoothies
Blend a smoothie with spinach, banana, and coconut water for a potassium-packed breakfast. You can also add protein powder or other ingredients to customize your smoothie to your liking.
Lunch Ideas
How can you make your lunch more potassium-rich? Incorporate potassium-rich foods into your midday meal.
Sweet Potato Salad
Make a sweet potato salad with roasted sweet potatoes, spinach, and a light vinaigrette dressing. Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of potassium, and spinach adds additional nutrients.
White Bean Soup
Enjoy a hearty white bean soup with vegetables like carrots, celery, and onions. White beans are high in potassium and protein.
Avocado Toast
Spread mashed avocado on whole-grain toast for a simple and nutritious lunch. Avocado is a great source of potassium and healthy fats.
Dinner Ideas
What are some satisfying potassium-rich dinner options? End your day with a delicious and nutritious dinner that includes plenty of potassium.
Salmon with Roasted Vegetables
Bake salmon with a side of roasted vegetables like potatoes, sweet potatoes, and beet greens. Salmon is a good source of potassium and omega-3 fatty acids, while the vegetables add fiber and vitamins.
Black Bean Burgers
Make black bean burgers and serve them on whole-wheat buns with your favorite toppings. Black beans are high in potassium and protein.
Spinach and Ricotta Stuffed Shells
Stuff jumbo pasta shells with a mixture of spinach, ricotta cheese, and herbs, then bake them in marinara sauce. Spinach is a good source of potassium, and ricotta cheese adds calcium and protein.
Snack Ideas
What are some quick and easy potassium-rich snacks? Keep these snacks on hand for a quick potassium boost between meals.
Dried Apricots
Dried apricots are a convenient and portable snack that is high in potassium. A small handful can provide a significant amount of potassium.
Banana with Nut Butter
Enjoy a banana with a tablespoon of nut butter, such as peanut butter or almond butter. This combination provides potassium, protein, and healthy fats.
Coconut Water
Sip on coconut water for a refreshing and hydrating snack that is also high in potassium.
6. Potassium and Specific Health Conditions
How does potassium intake affect certain health conditions? Understand the role of potassium in managing various health issues.
Kidney Disease
Can potassium intake affect kidney health? Potassium intake is a critical consideration for individuals with kidney disease.
Potassium and Kidney Function
In healthy individuals, the kidneys play a crucial role in regulating potassium levels in the body. However, in people with chronic kidney disease (CKD), the kidneys may not be able to effectively remove excess potassium, leading to hyperkalemia (high potassium levels). Managing potassium intake is essential to prevent complications.
Dietary Management
Individuals with CKD often need to follow a low-potassium diet. This involves limiting foods high in potassium, such as bananas, oranges, potatoes, and spinach. Portion control and proper food preparation techniques (like leaching potatoes) can also help reduce potassium content in meals.
Diabetes
How does potassium relate to diabetes management? Maintaining adequate potassium levels is important for individuals with diabetes.
Potassium and Insulin Sensitivity
Potassium plays a role in insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. Low potassium levels can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to poor blood sugar control. Ensuring adequate potassium intake can help improve insulin function and stabilize blood sugar levels.
Dietary Considerations
Individuals with diabetes should focus on consuming potassium-rich foods with a low glycemic index. Good choices include leafy greens, avocados, and berries. Monitoring carbohydrate intake is also important to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Can potassium help lower blood pressure? Potassium is a key nutrient in managing hypertension.
Potassium’s Role in Blood Pressure Regulation
Potassium helps regulate blood pressure by balancing the effects of sodium in the body. High sodium intake can lead to increased blood volume and elevated blood pressure, while adequate potassium intake helps counteract these effects.
Dietary Recommendations
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, which is rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy, emphasizes the importance of potassium in managing blood pressure. Consuming potassium-rich foods while reducing sodium intake can significantly lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
7. Debunking Common Myths About Potassium
Are there misconceptions about potassium that need clarification? Let’s address some common myths and misconceptions about potassium.
Myth: Bananas Are the Only Good Source of Potassium
Is this classic claim really true? While bananas are indeed a good source of potassium, they are not the only or even the best source. Many other fruits, vegetables, and foods contain higher levels of potassium.
Myth: You Need Supplements to Get Enough Potassium
Can you get enough potassium from food alone? For most healthy individuals, it is possible to obtain sufficient potassium through a balanced diet that includes a variety of potassium-rich foods. Supplements should only be considered under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Myth: High Potassium Intake Is Always Safe
Is there such a thing as too much potassium? While potassium is essential, excessive intake can be harmful, especially for individuals with kidney disease. High potassium levels (hyperkalemia) can lead to heart arrhythmias and other serious complications.
8. Practical Tips for Maximizing Potassium Intake
How can you ensure you’re getting enough potassium every day? Here are some actionable tips for maximizing your potassium intake.
Read Food Labels
Get in the habit of reading food labels to check the potassium content of packaged foods. This can help you make informed choices and select foods that are rich in potassium.
Plan Your Meals
Plan your meals in advance to ensure you’re including a variety of potassium-rich foods throughout the day. This can help you meet your daily potassium needs and maintain a balanced diet.
Choose Fresh Over Processed Foods
Opt for fresh, whole foods over processed foods whenever possible. Processed foods are often low in potassium and high in sodium, which can counteract the benefits of potassium.
Prepare Foods Properly
Certain cooking methods can affect the potassium content of foods. For example, boiling vegetables can leach potassium into the water. Steaming, roasting, or microwaving vegetables can help retain more potassium.
9. Delicious Recipes High in Potassium
What are some tasty ways to enjoy potassium-rich meals? Explore these recipes to add more potassium to your diet.
Sweet Potato and Black Bean Chili
Enjoy a hearty and nutritious chili packed with potassium. This recipe combines sweet potatoes, black beans, and a variety of spices for a flavorful meal.
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- 1 onion, chopped
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 red bell pepper, chopped
- 1 sweet potato, peeled and diced
- 1 can (15 ounces) black beans, rinsed and drained
- 1 can (14.5 ounces) diced tomatoes, undrained
- 1 cup vegetable broth
- 1 tablespoon chili powder
- 1 teaspoon cumin
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- Heat olive oil in a large pot over medium heat.
- Add onion and garlic and cook until softened.
- Add red bell pepper and sweet potato and cook for 5 minutes.
- Stir in black beans, diced tomatoes, vegetable broth, chili powder, and cumin.
- Bring to a boil, then reduce heat and simmer for 20 minutes, or until sweet potato is tender.
- Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Spinach and Salmon Salad
This salad is a powerhouse of nutrients, combining spinach, salmon, and other healthy ingredients.
Ingredients:
- 5 ounces spinach
- 4 ounces cooked salmon, flaked
- 1/4 cup red onion, thinly sliced
- 1/4 cup dried cranberries
- 1/4 cup walnuts, chopped
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- 1 tablespoon balsamic vinegar
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- In a large bowl, combine spinach, salmon, red onion, dried cranberries, and walnuts.
- In a small bowl, whisk together olive oil and balsamic vinegar.
- Pour dressing over salad and toss gently to combine.
- Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Banana and Avocado Smoothie
Start your day with a creamy and potassium-rich smoothie.
Ingredients:
- 1 banana
- 1/2 avocado
- 1 cup spinach
- 1 cup coconut water
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1 teaspoon honey (optional)
Instructions:
- Combine all ingredients in a blender.
- Blend until smooth.
- Add more coconut water if needed to reach desired consistency.
- Serve immediately.
10. Consulting a Healthcare Professional
When should you seek professional advice about your potassium intake? Know when to consult with a healthcare provider.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms of potassium deficiency or have concerns about your potassium levels, consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms, order blood tests to check your potassium levels, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Who Should Be Concerned
Certain individuals are at higher risk of potassium imbalances and should be particularly vigilant about monitoring their potassium levels. These include:
- Individuals with chronic kidney disease
- People taking diuretics or laxatives
- Individuals with diabetes
- People with gastrointestinal disorders
What to Discuss with Your Doctor
When you consult with your doctor, be prepared to discuss your diet, medications, and any underlying medical conditions. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs and circumstances.
FAQ About Foods High in Potassium
What are some frequently asked questions about potassium-rich foods? Here are some common questions and their answers.
1. What is the recommended daily intake of potassium?
The recommended daily intake of potassium for adults is typically between 3,500 and 4,700 milligrams. However, individual needs may vary depending on age, health status, and other factors.
2. Can you get too much potassium from food?
It is rare to get too much potassium from food alone. However, excessive intake from supplements can lead to hyperkalemia, especially in individuals with kidney disease.
3. Are potassium supplements safe?
Potassium supplements should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Excessive intake can be harmful, especially for individuals with kidney problems.
4. What are the best fruits for potassium?
Some of the best fruits for potassium include bananas, avocados, oranges, cantaloupe, and dried apricots.
5. What are the best vegetables for potassium?
Excellent vegetable sources of potassium include sweet potatoes, potatoes, spinach, beet greens, and white beans.
6. Does cooking affect the potassium content of foods?
Yes, certain cooking methods can affect the potassium content of foods. Boiling vegetables can leach potassium into the water, while steaming, roasting, or microwaving can help retain more potassium.
7. Can low potassium cause muscle cramps?
Yes, low potassium levels can lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue.
8. How can I increase my potassium intake if I don’t like bananas?
If you don’t like bananas, there are many other potassium-rich foods to choose from, such as sweet potatoes, avocados, spinach, and coconut water.
9. Is coconut water a good source of potassium?
Yes, coconut water is a natural electrolyte drink that is high in potassium, making it a great option for hydration and potassium replenishment.
10. What is the relationship between potassium and blood pressure?
Potassium helps regulate blood pressure by balancing the effects of sodium in the body. Adequate potassium intake can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Incorporating foods high in potassium into your diet is a crucial step toward maintaining optimal health. From supporting heart and muscle function to promoting bone and digestive health, potassium offers a wide range of benefits. By understanding which foods are rich in potassium and how to include them in your daily meals, you can take control of your health and well-being.
Ready to explore more delicious and nutritious recipes? Visit larosafoods.com today for a wealth of culinary inspiration and expert nutritional advice tailored to your needs. Whether you’re looking for quick and easy weeknight dinners or in-depth guides on specific ingredients, larosafoods.com is your go-to resource for all things food and wellness. Don’t wait – start your journey to a healthier, happier you with larosafoods.com today. Our address is 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States. You can also call us at +1 (415) 987-0123, or visit our website at larosafoods.com.


