Oatmeal is indeed a whole grain food, celebrated for its nutritional benefits and versatility in cooking, making it a fantastic choice for health-conscious individuals. This article from larosafoods.com will dive deep into the world of oatmeal, exploring its health benefits, nutritional profile, and various ways to incorporate it into your diet. Get ready to discover why oatmeal deserves a starring role in your pantry, offering both delicious meals and supporting overall wellness with its fiber content and complex carbohydrates.
1. What Defines a Whole Grain and Why Does It Matter?
Understanding what constitutes a whole grain is essential to appreciating the nutritional value of oatmeal.
1.1 Breaking Down the Anatomy of a Grain
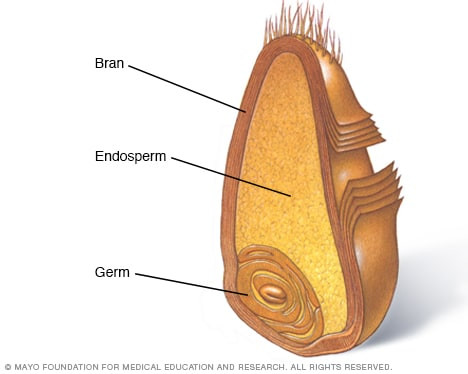
Grains, or cereals, are seeds of grasses cultivated for consumption, including familiar staples like wheat, oats, and rice. Each grain comprises three key components:
- Bran: The outer layer that’s rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Germ: The embryo of the seed, packed with vitamins, healthy fats, and essential nutrients.
- Endosperm: The energy reserve, mainly consisting of starches along with some proteins and vitamins, yet limited in fiber.
 Oatmeal whole grain anatomy
Oatmeal whole grain anatomy
1.2 Why Whole Grains Stand Out
Whole grains retain all three parts—bran, germ, and endosperm—offering a complete nutritional package that refined grains lack. According to the American Heart Association, this intact structure provides a superior source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which are vital for maintaining health. Choosing whole grains like oatmeal supports digestive health and helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
2. Oatmeal: A Whole Grain Champion
Oatmeal, derived from oat grains, is a prime example of a whole grain food.
2.1 What Makes Oatmeal a Whole Grain?
Oatmeal is processed in a way that retains the bran, germ, and endosperm, ensuring it provides all the nutritional benefits of the whole grain. Unlike refined grains where parts are removed, oatmeal keeps its natural fiber and nutrients intact.
2.2 Different Types of Oatmeal
- Steel-Cut Oats: These are the least processed, taking the longest to cook and offering a chewy texture.
- Rolled Oats (Old-Fashioned): Steamed and rolled to flatten them, they cook faster than steel-cut oats.
- Quick Oats: Further processed for even quicker cooking, but still retain whole grain benefits.
- Instant Oats: The most processed, often with added sugars and flavors, and cook almost instantly.
2.3 Nutritional Profile of Oatmeal Per Serving
| Nutrient | Amount (per 1/2 cup dry) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 150 |
| Protein | 5 grams |
| Fiber | 4 grams |
| Iron | 10% DV |
| Magnesium | 8% DV |
(DV = Daily Value)
3. Health Benefits of Oatmeal
Oatmeal’s status as a whole grain powerhouse translates into numerous health advantages.
3.1 Cardiovascular Health
The soluble fiber in oatmeal, particularly beta-glucan, is renowned for its cholesterol-lowering capabilities. Research indicates that regular consumption of oatmeal can reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, thereby decreasing the risk of heart disease.
3.2 Blood Sugar Control
Oatmeal has a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to many refined grains, meaning it causes a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This makes it an excellent choice for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar.
3.3 Weight Management
The high fiber content in oatmeal promotes satiety, helping you feel fuller for longer and reducing overall calorie intake. This can be a significant advantage for weight management and preventing overeating.
3.4 Digestive Health
Fiber is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Oatmeal’s fiber content aids in preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Additionally, it supports a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for overall health.
3.5 Rich in Antioxidants
Oatmeal contains antioxidants, including avenanthramides, which are unique to oats. These compounds have anti-inflammatory and anti-itching effects, potentially protecting against chronic diseases.
4. Incorporating Oatmeal into Your Diet
Oatmeal is incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in numerous ways.
4.1 Classic Oatmeal Recipes
- Basic Oatmeal: Cook oatmeal with water or milk and top with fruits, nuts, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup.
- Overnight Oats: Combine oats with milk (dairy or non-dairy), yogurt, and your favorite toppings. Let it sit in the fridge overnight for a grab-and-go breakfast.
- Baked Oatmeal: A comforting and customizable dish that can be made ahead of time. Add fruits, nuts, and spices for a delicious and healthy breakfast or brunch.
4.2 Creative Uses of Oatmeal
- Oat Flour: Grind oatmeal into a flour to use in baking recipes, adding a nutritious boost to muffins, pancakes, and bread.
- Oatmeal in Smoothies: Add a scoop of oatmeal to your smoothie for extra fiber and thickness.
- Oatmeal as a Meat Binder: Use cooked oatmeal or oat flour as a binder in meatloaf or veggie burgers.
- Oatmeal in Granola: Add oats to your homemade granola for a hearty and healthy snack.
4.3 Oatmeal Recipe Example Table
| Recipe Idea | Ingredients | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Classic Oatmeal | Oats, milk/water, fruit, nuts, honey | Cook oats with liquid, top with fruit, nuts, and honey. |
| Overnight Oats | Oats, milk, yogurt, chia seeds, fruit | Combine ingredients in a jar, refrigerate overnight. |
| Oatmeal Smoothie | Oats, banana, spinach, milk, protein powder | Blend all ingredients until smooth. |
5. Reading Labels: How to Choose the Best Oatmeal
Navigating the grocery store aisles can be confusing, but knowing how to read labels will help you choose the best oatmeal.
5.1 What to Look For
- Ingredients: Look for oatmeal with minimal added ingredients. Plain oats should be the primary ingredient.
- Fiber Content: Check the fiber content per serving. Aim for oatmeal with at least 3-4 grams of fiber per serving.
- Added Sugars: Be wary of instant oatmeal varieties that often contain high amounts of added sugars.
5.2 Understanding Marketing Terms
- “Whole Grain”: Ensures that the product contains all parts of the grain.
- “Multigrain”: Simply means the product contains more than one type of grain, not necessarily whole grains.
- “Fortified”: Indicates that extra nutrients have been added, which can be beneficial but doesn’t replace the natural nutrients of whole grains.
6. Debunking Common Oatmeal Myths
Let’s clear up some common misconceptions about oatmeal.
6.1 Myth: Oatmeal is Boring
Reality: Oatmeal is a blank canvas for flavor. Experiment with different toppings, spices, and mix-ins to create endless variations.
6.2 Myth: Instant Oatmeal is Just as Good as Other Types
Reality: While instant oatmeal can be convenient, it often contains added sugars and less fiber compared to steel-cut or rolled oats.
6.3 Myth: Oatmeal is Only for Breakfast
Reality: Oatmeal can be enjoyed at any time of day. Use it in baking, smoothies, or as a side dish for a nutritious boost.
7. Potential Downsides of Oatmeal
While oatmeal is generally healthy, there are a few considerations.
7.1 Phytic Acid
Oatmeal contains phytic acid, which can inhibit the absorption of certain minerals like iron and zinc. Soaking oats before cooking can help reduce phytic acid levels.
7.2 Gluten Content
Oats are naturally gluten-free, but they can be contaminated with gluten during processing. If you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, choose certified gluten-free oats.
7.3 Portion Control
While oatmeal is healthy, it’s still calorie-dense. Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating.
8. Oatmeal vs. Other Whole Grains
How does oatmeal stack up against other popular whole grains?
8.1 Nutritional Comparison
| Grain | Calories (per 1/2 cup cooked) | Fiber (grams) | Protein (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oatmeal | 83 | 2 | 3 |
| Quinoa | 111 | 3 | 4 |
| Brown Rice | 109 | 2 | 2 |
8.2 Unique Benefits
- Oatmeal: Known for its cholesterol-lowering properties and creamy texture.
- Quinoa: A complete protein source, making it a great option for vegetarians and vegans.
- Brown Rice: Versatile and a good source of manganese and selenium.
9. Expert Opinions on Oatmeal
Nutritionists and dietitians widely recommend oatmeal as part of a balanced diet.
9.1 Quotes from Experts
- “Oatmeal is a fantastic source of soluble fiber, which is crucial for heart health,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a registered dietitian at the University of California, Berkeley.
- “I always recommend oatmeal to my patients looking to improve their blood sugar control. It’s a slow-digesting carbohydrate that keeps you full and energized,” adds Chef James Oliver, a culinary expert focused on healthy eating.
9.2 Studies and Research
Numerous studies support the health benefits of oatmeal. For instance, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming oatmeal regularly can significantly reduce LDL cholesterol levels.
10. Oatmeal and Specific Dietary Needs
Oatmeal can be a beneficial addition to various specialized diets.
10.1 Gluten-Free Diet
Ensure you choose certified gluten-free oats to avoid cross-contamination. Oatmeal is a versatile and nutritious option for those following a gluten-free diet.
10.2 Vegan Diet
Oatmeal is naturally vegan and can be paired with plant-based milk and toppings for a satisfying and nutritious meal.
10.3 Low-Sugar Diet
Opt for plain oatmeal and sweeten it with natural alternatives like berries, cinnamon, or a touch of stevia to keep the sugar content low.
11. Finding Inspiration at larosafoods.com
Looking for more ways to incorporate oatmeal into your diet? Look no further than larosafoods.com!
11.1 Explore Our Recipe Collection
At larosafoods.com, you’ll find a diverse collection of oatmeal recipes, from classic preparations to innovative dishes that showcase the versatility of this whole grain.
11.2 Discover Expert Tips and Tricks
Our website features expert tips and tricks for cooking with oatmeal, including advice on choosing the right type of oats, maximizing its nutritional benefits, and creating delicious flavor combinations.
11.3 Join Our Community
Connect with fellow food enthusiasts in our online community. Share your favorite oatmeal recipes, ask questions, and get inspired by others who are passionate about healthy eating.
12. Is Oatmeal A Whole Grain Food? FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about oatmeal and its status as a whole grain food:
12.1 Is all oatmeal considered a whole grain?
Yes, all types of oatmeal, including steel-cut, rolled, quick, and instant oats, are considered whole grains as they contain all parts of the oat kernel.
12.2 Can oatmeal help lower cholesterol?
Yes, the soluble fiber in oatmeal, particularly beta-glucan, has been shown to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
12.3 Is oatmeal good for weight loss?
Yes, oatmeal is high in fiber, which promotes satiety and can help with weight management.
12.4 Does oatmeal contain gluten?
Oats are naturally gluten-free, but they can be contaminated during processing. Look for certified gluten-free oats if you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
12.5 Can I eat oatmeal every day?
Yes, eating oatmeal every day can be part of a healthy diet, providing fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
12.6 How can I make oatmeal taste better?
Experiment with different toppings like fruits, nuts, seeds, spices, and natural sweeteners to enhance the flavor of oatmeal.
12.7 Is instant oatmeal as healthy as other types of oatmeal?
Instant oatmeal is convenient but may contain added sugars and less fiber than steel-cut or rolled oats. Opt for plain varieties and add your own toppings.
12.8 What are the best toppings for oatmeal?
Healthy and delicious toppings for oatmeal include berries, bananas, nuts, seeds, cinnamon, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup.
12.9 Can oatmeal help with digestive health?
Yes, the fiber in oatmeal can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements.
12.10 How should I store oatmeal?
Store oatmeal in a cool, dry place in an airtight container to maintain its freshness.
13. Conclusion: Embrace the Goodness of Oatmeal
Oatmeal is undeniably a whole grain food that offers a wealth of health benefits and culinary possibilities. From supporting heart health and managing blood sugar to aiding in weight management and promoting digestive wellness, oatmeal is a nutritional powerhouse. By understanding its various forms, learning how to read labels, and experimenting with different recipes, you can make oatmeal a delicious and integral part of your daily diet. Head over to larosafoods.com to discover a treasure trove of oatmeal recipes, expert tips, and a vibrant community of food lovers. Embrace the goodness of oatmeal and embark on a journey towards a healthier and more delicious lifestyle today!
Ready to explore the world of oatmeal and discover exciting new recipes? Visit larosafoods.com now and unlock a wealth of culinary inspiration. Join our community, share your creations, and let’s celebrate the delicious and nutritious potential of oatmeal together! You can also visit our location at 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States or call us at +1 (415) 987-0123 for more information. Let larosafoods.com be your guide to a healthier and more flavorful life!


