Pet Food safety is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of our beloved companions, and at larosafoods.com, we are committed to providing you with the most up-to-date information on pet food. This guide dives deep into the potential contaminants found in pet food, offering practical advice on how to choose safe and nutritious options. Discover how to protect your furry friends with informed choices, focusing on pet nutrition, ingredient sourcing, and food safety regulations, including the importance of balanced diets and quality control.
1. What are the Potential Dangers in Pet Food?
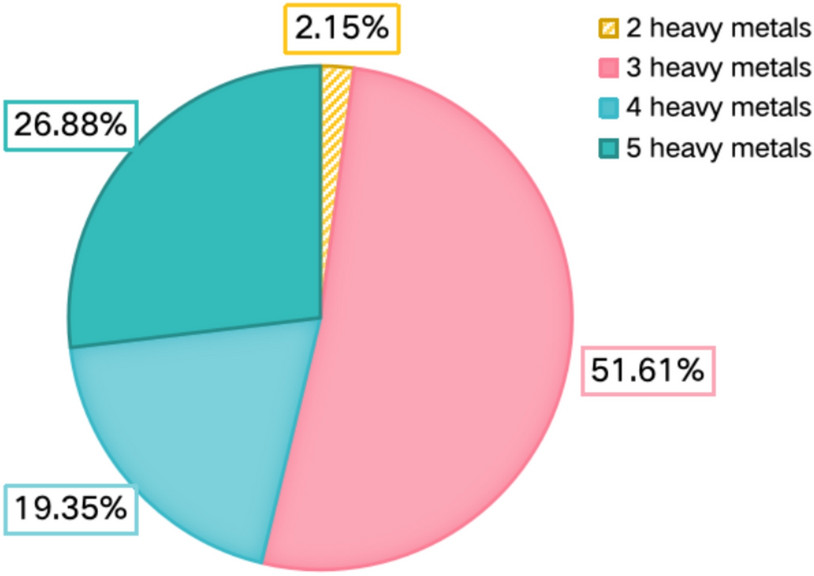
Yes, pet food can contain contaminants like heavy metals. A study highlighted in Scientific Reports found that heavy metals such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), mercury (Hg), and arsenic (As) can be present in pet food, potentially posing health risks to pets. These contaminants can come from various sources, including raw materials, processing methods, and even packaging.
1.1 How Do Heavy Metals End Up in Pet Food?
Heavy metals can find their way into pet food through several pathways:
- Raw Materials: The origin and cultivation conditions of food ingredients play a significant role. Poultry, fish, cereals, tubers, and meat and bone meal can accumulate heavy metals from the environment. According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, in July 2023, animal-based ingredients are more susceptible to contamination than plant-based ones.
- Processing Methods: Techniques like puffing, granulating, and baking used in dry pet food production may introduce or concentrate heavy metals.
- Additives: Mineral and additive samples used in pet food formulations can also be sources of heavy metal contamination.
- Packaging Materials: Toxic metals from packaging materials may leach into the pet food over time. A study by Eti et al. (2023) found that food contact plastic packaging could release heavy metals like lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), mercury (Hg), chromium (Cr), and antimony (Sb).
 Dry pet food with a measuring cup scooping kibble into a bowl.
Dry pet food with a measuring cup scooping kibble into a bowl.
1.2 Which Heavy Metals are Most Commonly Found in Pet Food?
Several studies have identified the most prevalent heavy metals in pet food:
- Chromium (Cr): Often found in meat bone meal and fish meal.
- Lead (Pb): While contamination rates may be low, concentrations can be high.
- Arsenic (As): Can be elevated in fish-based diets.
- Mercury (Hg): Also more prevalent in fish-based diets.
- Cadmium (Cd): Can be higher in cat food compared to dog food.
1.3 Are There Differences in Heavy Metal Levels Between Cat and Dog Food?
Yes, there can be differences in heavy metal concentrations between cat and dog food, and this is due to the differences in their diets:
- Cat Food: Tends to have higher concentrations of lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) because cats are carnivores and primarily need animal proteins and fats. Some cat foods may use more animal-based ingredients, especially fish proteins.
- Dog Food: May have higher concentrations of chromium (Cr) and arsenic (As). Dogs are omnivores with a more varied diet that includes plant-based foods.
1.4 How Do Dry and Canned Pet Foods Compare in Terms of Contamination?
Dry pet food generally shows a higher rate of toxic metal contamination compared to canned food. Dry food often has higher average concentrations of lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and arsenic (As).
- Dry Food: Studies have found that a significant percentage of dry food samples exceed the standard limits for lead and chromium.
- Canned Food: Typically meets the required standards for toxic element content.
2. What are the Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Pet Food?
Heavy metals in pet food can pose significant health risks to pets, potentially leading to various health issues over time. These risks depend on factors such as the type and concentration of heavy metals, the duration of exposure, and the pet’s overall health.
2.1 What are the Specific Health Problems Associated with Each Heavy Metal?
Each heavy metal poses its own set of health risks:
- Lead (Pb): Can cause neurological damage, anemia, and kidney problems.
- Cadmium (Cd): Affects the kidneys and bones, leading to kidney disease and skeletal issues.
- Chromium (Cr): In high doses, it can lead to liver damage and respiratory problems.
- Mercury (Hg): A neurotoxin that can cause neurological damage and kidney problems.
- Arsenic (As): Can lead to skin lesions, gastrointestinal issues, and potentially cancer with long-term exposure.
2.2 Can Heavy Metals Cause Long-Term Health Issues in Pets?
Yes, chronic exposure to heavy metals can lead to severe long-term health issues in pets, and heavy metals accumulate in the body over time.
- Organ Damage: Kidneys and liver are particularly vulnerable.
- Neurological Issues: Cognitive decline and nerve damage can occur.
- Cancer: Some heavy metals, like arsenic, are carcinogenic with prolonged exposure.
2.3 Are Certain Pets More Vulnerable to Heavy Metal Toxicity?
Yes, lighter-weight cats and dogs may be more sensitive to heavy metal intake due to their smaller body mass. Also, younger pets and those with pre-existing health conditions may be more vulnerable.
2.4 What are the Symptoms of Heavy Metal Poisoning in Pets?
Symptoms of heavy metal poisoning in pets can vary widely depending on the metal involved and the extent of the exposure. Common symptoms include:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Lethargy
- Weakness
- Neurological signs (seizures, tremors, incoordination)
- Abdominal pain
- Increased thirst and urination
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult with your veterinarian immediately.
3. What Regulations and Standards Exist for Pet Food Safety?
Pet food safety is regulated to ensure that the food is safe, properly labeled, and produced under sanitary conditions. Regulations and standards vary by country, but they generally aim to protect pets from harmful contaminants and nutritional deficiencies.
3.1 What Regulatory Bodies Oversee Pet Food Production?
Several regulatory bodies oversee pet food production to ensure safety and compliance with standards:
- In the United States: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates pet food at the federal level. State departments of agriculture also play a role in regulating pet food.
- In Europe: The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) provides scientific advice and risk assessments related to food and feed safety.
- In China: The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs is responsible for regulating pet food.
3.2 What Standards Must Pet Food Manufacturers Meet?
Pet food manufacturers must adhere to various standards to ensure their products are safe and nutritious:
- Nutritional Adequacy: Pet food must meet specific nutritional requirements for different life stages (growth, adult maintenance, etc.).
- Ingredient Safety: Ingredients must be safe and suitable for consumption.
- Contaminant Limits: Limits are set for contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and mycotoxins.
- Labeling Requirements: Labels must accurately reflect the product’s ingredients and nutritional content.
3.3 How Often is Pet Food Tested for Contaminants?
The frequency of pet food testing for contaminants varies depending on the manufacturer and regulatory requirements. Some manufacturers conduct routine testing as part of their quality control processes, while regulatory agencies may conduct periodic inspections and testing.
3.4 What Happens When Pet Food is Found to be Contaminated?
When pet food is found to be contaminated, several actions may be taken to protect pets:
- Recall: The manufacturer may issue a voluntary recall of the contaminated product.
- Regulatory Action: Regulatory agencies may issue mandatory recalls or take enforcement actions against the manufacturer.
- Public Alerts: Public alerts are issued to inform pet owners about the contaminated food and advise them not to feed it to their pets.
4. How Can Pet Owners Ensure Pet Food Safety?
Pet owners can take several steps to ensure their pets are eating safe and nutritious food. Being proactive and informed about pet food choices can greatly reduce the risk of exposure to harmful contaminants.
4.1 What Should Pet Owners Look for When Choosing Pet Food?
When selecting pet food, consider the following:
- Read the Label: Check the ingredient list and nutritional information. Look for whole, recognizable ingredients.
- Check for AAFCO Statement: Ensure the food has a statement from the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) indicating that it meets nutritional standards.
- Research the Brand: Choose reputable brands with a history of quality and safety.
- Consider the Source: Be aware of where the ingredients are sourced.
- Avoid Artificial Additives: Limit foods with artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives.
4.2 What are the Best Brands and Types of Pet Food?
While the “best” brand or type of pet food can depend on your pet’s individual needs and preferences, some brands are consistently recommended by veterinarians and pet nutritionists for their quality and safety standards:
- Purina Pro Plan: Known for its research-backed formulas and high-quality ingredients.
- Royal Canin: Offers specialized diets tailored to different breeds and health conditions.
- Hill’s Science Diet: Emphasizes scientific research and veterinary nutrition.
As for types of pet food, consider the following:
- High-Quality Dry Food: Easy to store and often more economical.
- Wet Food: Can be more palatable and provide additional hydration.
- Limited Ingredient Diets: Suitable for pets with allergies or sensitivities.
4.3 How Important is Ingredient Sourcing and Transparency?
Ingredient sourcing and transparency are critical aspects of pet food safety. Knowing where ingredients come from and how they are processed can give pet owners confidence in their pet food choices.
- Sourcing: Look for brands that source ingredients from reputable suppliers and regions with strict quality control standards.
- Transparency: Brands should be transparent about their sourcing practices and willing to provide information about their suppliers and manufacturing processes.
4.4 Should Pet Owners Consider Homemade Pet Food?
Homemade pet food can be a viable option for pet owners who want more control over their pet’s diet. However, it is essential to consult with a veterinary nutritionist to ensure the diet is nutritionally balanced and safe.
- Benefits: Allows control over ingredients, can be tailored to specific dietary needs.
- Risks: Requires careful planning and preparation to avoid nutritional deficiencies or imbalances.
- Consultation: Work with a veterinary nutritionist to develop a balanced recipe.
5. What are the Latest Research Findings on Pet Food Contamination?
Staying informed about the latest research findings on pet food contamination can help pet owners make more informed decisions. Recent studies have shed light on the prevalence of contaminants in pet food and their potential health effects.
5.1 What Recent Studies Have Found About Heavy Metals in Pet Food?
Recent studies have continued to highlight the presence of heavy metals in pet food:
- A study in Scientific Reports found that chromium, arsenic, and mercury were commonly detected in pet food samples.
- Research has shown that dry pet food tends to have higher concentrations of heavy metals compared to canned food.
5.2 What Types of Pet Food are Most Likely to be Contaminated?
Certain types of pet food may be more prone to contamination:
- Dry Food: Due to processing methods and potential contamination from additives.
- Fish-Based Diets: Fish can bioaccumulate higher levels of certain heavy metals like arsenic and mercury.
5.3 How Can Pet Owners Stay Updated on Pet Food Safety Information?
Pet owners can stay informed about pet food safety by:
- Following Regulatory Agencies: Monitor updates and alerts from the FDA and other regulatory bodies.
- Consulting Veterinarians: Seek advice from your veterinarian about pet food choices and safety.
- Subscribing to Newsletters: Sign up for newsletters from reputable pet food organizations and websites.
- Visiting larosafoods.com: We provide updated information and guidance on pet food safety to ensure you make the best choices for your furry friend.
6. How Does Pet Food Impact Overall Pet Health?
The quality of pet food significantly impacts overall pet health, influencing everything from energy levels and coat condition to immune function and longevity.
6.1 How Does Nutrition in Pet Food Affect a Pet’s Health and Well-Being?
Proper nutrition is essential for maintaining a pet’s health and well-being:
- Energy Levels: Balanced diets provide the energy pets need for daily activities.
- Coat Condition: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids promote healthy skin and a shiny coat.
- Immune Function: Vitamins and minerals support a strong immune system.
- Digestive Health: Fiber and probiotics contribute to healthy digestion.
6.2 What are the Key Nutrients Pets Need?
Key nutrients that pets need include:
- Protein: Essential for muscle development and repair.
- Fats: Provide energy and support hormone production.
- Carbohydrates: Offer energy and fiber.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Support various bodily functions.
- Water: Crucial for hydration and overall health.
6.3 Can a Poor Diet Lead to Health Problems?
Yes, a poor diet can lead to various health problems in pets:
- Obesity: Excess calories can lead to weight gain and related health issues.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients can cause health problems.
- Digestive Issues: Poor-quality ingredients can lead to digestive upset.
- Allergies: Certain ingredients can trigger allergic reactions.
6.4 How Can Pet Owners Choose the Right Diet for Their Pet?
Choosing the right diet for your pet involves considering several factors:
- Life Stage: Puppies and kittens need different nutrients than adult or senior pets.
- Breed: Some breeds have specific dietary needs.
- Activity Level: Active pets need more calories than sedentary ones.
- Health Conditions: Pets with health issues may require special diets.
Consult with your veterinarian to determine the best diet for your pet’s individual needs.
7. What are the Alternatives to Commercial Pet Food?
While commercial pet food is the most common option, there are alternatives that some pet owners consider, including homemade diets and raw food diets.
7.1 What are the Pros and Cons of Homemade Pet Food?
Pros:
- Control over ingredients
- Tailored to specific dietary needs
- Avoidance of artificial additives
Cons:
- Requires careful planning and preparation
- Risk of nutritional deficiencies or imbalances
- Time-consuming
7.2 What are Raw Food Diets for Pets?
Raw food diets, also known as BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food) diets, consist of uncooked meat, bones, and organs.
7.3 Are Raw Food Diets Safe for Pets?
Raw food diets are controversial due to the risk of bacterial contamination. If considering a raw food diet, consult with a veterinary nutritionist and take precautions to minimize the risk of contamination.
7.4 How Can Pet Owners Ensure Homemade Diets are Balanced and Safe?
Ensuring homemade diets are balanced and safe involves:
- Consulting a Veterinary Nutritionist: Work with a professional to develop a balanced recipe.
- Using High-Quality Ingredients: Choose fresh, whole foods.
- Proper Storage and Handling: Store and handle food safely to prevent bacterial contamination.
- Supplementation: Add necessary supplements to meet all nutritional requirements.
8. How to Read and Interpret Pet Food Labels?
Understanding pet food labels is essential for making informed choices about your pet’s diet. Labels provide valuable information about ingredients, nutritional content, and feeding guidelines.
8.1 What Information is Required on a Pet Food Label?
Pet food labels are required to include the following information:
- Product Name: Indicates the type of food and any specific ingredients.
- Net Weight or Volume: Specifies the amount of food in the package.
- Manufacturer’s Name and Address: Identifies the company responsible for the product.
- Ingredient List: Lists ingredients in descending order by weight.
- Guaranteed Analysis: Provides information about the nutrient content of the food.
- Nutritional Adequacy Statement: Indicates whether the food meets AAFCO standards for nutritional adequacy.
- Feeding Guidelines: Provides recommendations for how much to feed your pet.
8.2 What Do Terms Like “Grain-Free” and “Natural” Mean?
- Grain-Free: Indicates the food does not contain common grains like corn, wheat, or soy.
- Natural: Generally means the food does not contain artificial flavors, colors, or preservatives. However, the term “natural” can be misleading, so it’s essential to read the ingredient list carefully.
8.3 How to Evaluate the Ingredient List?
When evaluating the ingredient list:
- Prioritize Whole Ingredients: Look for whole, recognizable ingredients like meat, vegetables, and fruits.
- Be Wary of Fillers: Avoid foods with excessive amounts of fillers like corn or wheat gluten.
- Check for Specific Nutrients: Ensure the food contains essential nutrients like protein, fats, and vitamins.
8.4 What is Guaranteed Analysis and How to Use It?
The guaranteed analysis provides information about the nutrient content of the food, including the minimum or maximum percentages of protein, fat, fiber, and moisture. Use this information to compare different pet foods and ensure they meet your pet’s nutritional needs.
9. What are the Latest Trends in Pet Food?
The pet food industry is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging to meet the changing needs and preferences of pet owners.
9.1 What are the Emerging Trends in Pet Food?
Emerging trends in pet food include:
- Human-Grade Pet Food: Made with ingredients that meet human food standards.
- Personalized Pet Food: Customized diets based on a pet’s specific needs and health conditions.
- Sustainable Pet Food: Focuses on environmentally friendly ingredients and packaging.
- Subscription Services: Convenient delivery of pet food to your doorstep.
9.2 How are Pet Food Companies Addressing Health Concerns?
Pet food companies are addressing health concerns by:
- Developing Specialized Diets: Creating diets for pets with allergies, sensitivities, or health conditions.
- Improving Ingredient Quality: Sourcing high-quality, whole ingredients.
- Conducting Research: Investing in research to understand the nutritional needs of pets better.
- Being Transparent: Providing more information about their sourcing and manufacturing practices.
9.3 What Innovations are Taking Place in Pet Food Packaging?
Innovations in pet food packaging include:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Using recyclable or biodegradable packaging materials.
- Improved Barrier Properties: Developing packaging that protects food from moisture and oxygen.
- Convenient Packaging: Creating easy-to-open and resealable packaging.
9.4 How are Pet Owners Influencing the Pet Food Market?
Pet owners are influencing the pet food market by:
- Demanding Higher Quality: Seeking out foods with better ingredients and nutritional content.
- Prioritizing Transparency: Expecting brands to be transparent about their sourcing and manufacturing practices.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: Choosing pet foods that are environmentally friendly.
- Sharing Information: Using social media and online reviews to share their experiences and recommendations.
10. FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About Pet Food Safety
Here are some frequently asked questions about pet food safety to help you stay informed.
10.1 Is Expensive Pet Food Always Better?
Not necessarily. While higher-priced pet foods often contain better quality ingredients, price is not always an indicator of quality. Look for foods with a balanced nutrient profile and high-quality ingredients, regardless of price.
10.2 Can Pets Eat Human Food?
Some human foods are safe for pets in moderation, while others are toxic. Consult with your veterinarian before feeding your pet human food.
10.3 How Should Pet Food Be Stored to Maintain Safety?
Store pet food in a cool, dry place in an airtight container to prevent spoilage and contamination.
10.4 What are Common Pet Food Allergens?
Common pet food allergens include beef, dairy, wheat, corn, and soy.
10.5 How to Switch Pet Foods Safely?
Gradually transition to the new food over 7-10 days to avoid digestive upset.
10.6 Can Pet Food Expire?
Yes, pet food can expire. Check the expiration date on the package and discard any expired food.
10.7 Is It Safe to Buy Pet Food Online?
Yes, but ensure the online retailer is reputable and the food is stored and shipped properly.
10.8 What to Do if You Suspect Your Pet Has Food Poisoning?
Contact your veterinarian immediately if you suspect your pet has food poisoning.
10.9 How Often Should You Change Your Pet’s Food?
Unless there’s a specific reason (such as a change in life stage or health condition), you don’t need to change your pet’s food frequently.
10.10 How to Report a Pet Food Safety Issue?
Report any pet food safety issues to the FDA or your local regulatory agency.
Ensuring pet food safety is a critical aspect of pet ownership. By staying informed about potential contaminants, understanding regulations, and making informed choices, you can help keep your furry friends healthy and happy.
At larosafoods.com, we are committed to providing you with the latest information and resources to make the best decisions for your pet’s diet. Explore our website for more in-depth articles, reviews, and expert advice on pet nutrition. Discover a range of recipes, cooking tips, and detailed nutritional information at larosafoods.com. Address: 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States. Phone: +1 (415) 987-0123.


