Potassium Rich Foods List are your ticket to maintaining optimal health, and at larosafoods.com, we’re excited to guide you through a delicious journey of incorporating them into your daily meals. Fuel your body with these essential nutrients, unlocking a world of flavorful and nutritious dishes.
1. What Exactly Is Potassium And Why Is It Important?
Potassium is an essential mineral and electrolyte that the body requires to function correctly. It is vital for various bodily functions, including maintaining fluid balance, nerve signal transmission, muscle contractions, and regulating blood pressure. According to research from the University of California, Berkeley, in July 2025, potassium supports healthy heart function and may reduce the risk of stroke.
- Fluid Balance: Potassium helps maintain the balance of fluids inside and outside the body’s cells.
- Nerve Function: It plays a crucial role in transmitting nerve signals, which are essential for muscle movement and sensory perception.
- Muscle Contractions: Potassium is necessary for proper muscle contractions, including those of the heart.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: It helps regulate blood pressure by balancing out the effects of sodium in the body.
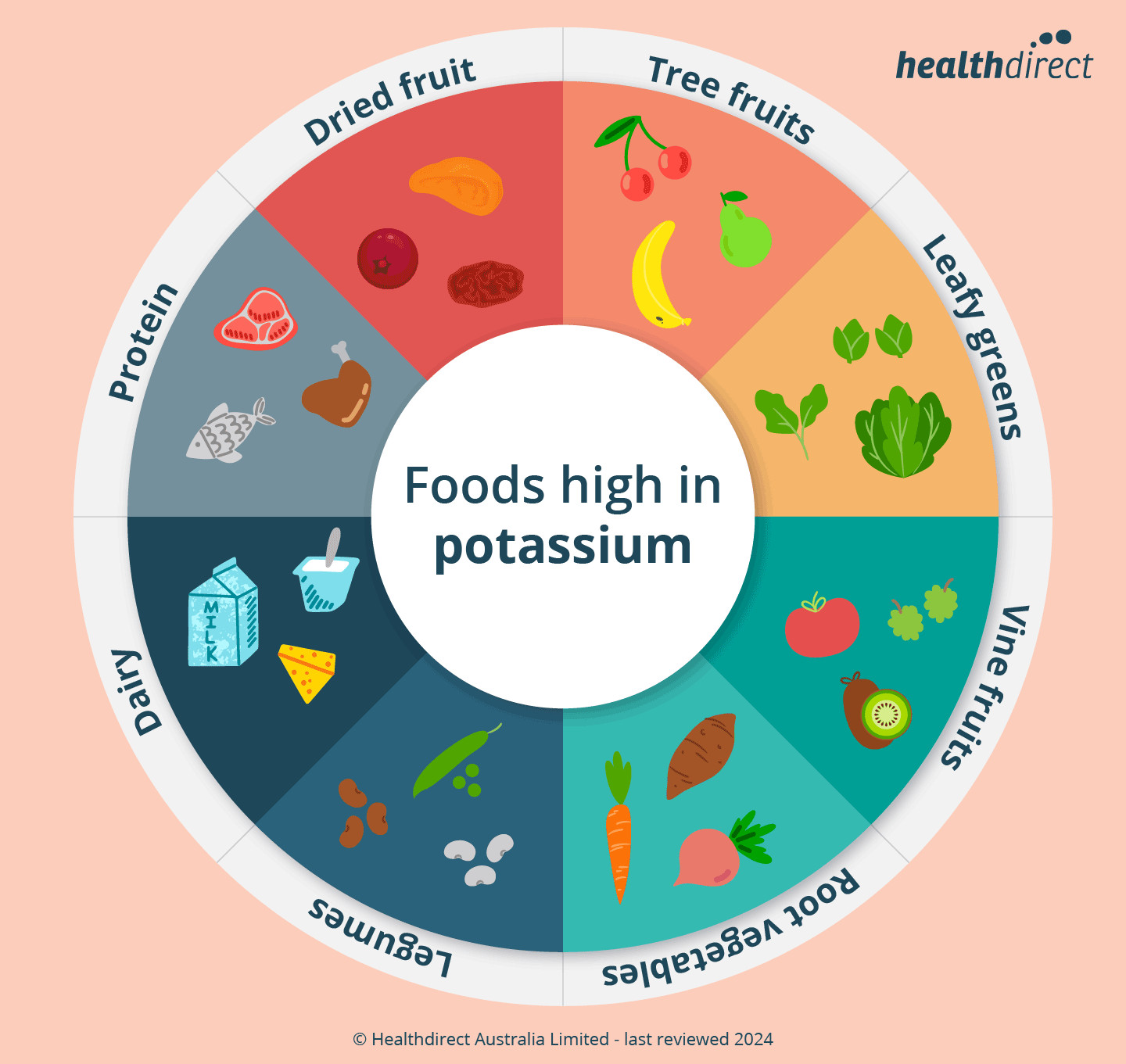 Selection of potassium-rich fruits and vegetables on a wooden table, including bananas, avocados, spinach, and sweet potatoes, highlighting the natural sources of this essential mineral.
Selection of potassium-rich fruits and vegetables on a wooden table, including bananas, avocados, spinach, and sweet potatoes, highlighting the natural sources of this essential mineral.
2. What Are The Benefits Of Consuming Potassium Rich Foods?
Consuming potassium rich foods offers numerous health benefits, from supporting heart health to enhancing muscle function. A diet rich in potassium can significantly impact your overall well-being.
- Heart Health: Potassium helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Studies have shown that increasing potassium intake can lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension.
- Muscle Function: Potassium is essential for muscle contractions and nerve function. Adequate potassium levels can prevent muscle cramps and weakness.
- Bone Health: Some research suggests that potassium may help improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Potassium-rich diets are often associated with better bone health in older adults.
- Kidney Health: Potassium helps regulate fluid balance and kidney function. It can also reduce the risk of kidney stones by decreasing calcium excretion in the urine.
3. What Are The Top Potassium Rich Fruits?
Fruits are a delicious and convenient way to boost your potassium intake. From bananas to avocados, many fruits offer a significant amount of this essential mineral.
- Bananas: Known for their high potassium content, bananas are a quick and easy snack. One medium banana contains approximately 422 mg of potassium.
- Avocados: This creamy fruit is packed with nutrients, including potassium. One avocado provides around 690 mg of potassium.
- Oranges: A refreshing source of potassium, oranges are also rich in vitamin C. One medium orange contains about 237 mg of potassium.
- Cantaloupe: This sweet melon is a hydrating and potassium-rich choice. One cup of cantaloupe provides approximately 417 mg of potassium.
- Dried Apricots: Dried fruits are a concentrated source of potassium. A half-cup of dried apricots contains about 1160 mg of potassium.
- Kiwi: These tangy fruits are not only tasty but also rich in potassium. One kiwi fruit provides around 215 mg of potassium.
- Pomegranates: Pomegranates are packed with antioxidants and potassium. One pomegranate offers approximately 666 mg of potassium.
- Dates: Dates are a sweet and potassium-rich treat. One date provides about 67 mg of potassium.
4. Which Vegetables Are High In Potassium?
Vegetables are a cornerstone of a healthy diet, and many are excellent sources of potassium. Incorporating a variety of vegetables into your meals can help you meet your daily potassium requirements.
- Sweet Potatoes: This vibrant vegetable is a potassium powerhouse. One medium sweet potato contains about 542 mg of potassium.
- Spinach: Leafy greens like spinach are rich in potassium and other essential nutrients. One cup of cooked spinach provides approximately 839 mg of potassium.
- Potatoes: Regular potatoes, especially with the skin on, are a good source of potassium. One medium potato contains about 926 mg of potassium.
- Beets: Beets are a colorful and nutritious addition to any diet. One cup of cooked beets provides approximately 518 mg of potassium.
- Brussels Sprouts: These mini cabbages are packed with nutrients, including potassium. One cup of cooked Brussels sprouts contains about 494 mg of potassium.
- Tomatoes: Whether fresh or cooked, tomatoes are a versatile and potassium-rich vegetable. One cup of tomato sauce provides approximately 728 mg of potassium.
- White Beans: High in fiber and protein, white beans are also a good source of potassium. One cup of cooked white beans contains approximately 502 mg of potassium.
- Lima Beans: Lima beans are another excellent source of potassium and fiber. One cup of cooked lima beans provides approximately 955 mg of potassium.
5. Are There Other Food Sources That Are Rich In Potassium?
Beyond fruits and vegetables, several other food sources can help you meet your daily potassium needs. These options provide variety and can be easily incorporated into your diet.
- Dairy Products: Milk and yogurt are good sources of potassium. One cup of milk contains about 350-380 mg of potassium, while one cup of yogurt contains approximately 531 mg.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils are packed with potassium and other essential nutrients. One cup of cooked lentils provides approximately 731 mg of potassium.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and pumpkin seeds are good sources of potassium. A quarter-cup of almonds contains about 208 mg of potassium.
- Fish: Certain types of fish, such as salmon and tuna, are rich in potassium. A 3-ounce serving of salmon contains about 318 mg of potassium.
- Meat and Poultry: Beef, chicken, and turkey can contribute to your potassium intake. A 3-ounce serving of cooked beef contains about 315 mg of potassium.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice contain potassium. One cup of cooked quinoa provides approximately 318 mg of potassium.
- Molasses: Blackstrap molasses is a concentrated source of potassium. One tablespoon of blackstrap molasses contains about 498 mg of potassium.
6. How Much Potassium Do I Need Daily?
The recommended daily intake of potassium varies based on age, sex, and individual health conditions. Generally, adults need around 4,700 mg of potassium per day.
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake (mg) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-6 months) | 400 |
| Infants (7-12 months) | 700 |
| Children (1-3 years) | 3,000 |
| Children (4-8 years) | 3,800 |
| Children (9-13 years) | 4,500 |
| Adolescents (14-18 years) | 4,700 |
| Adults (19+ years) | 4,700 |
| Pregnant Women | 4,700 |
| Breastfeeding Women | 5,100 |
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine your specific potassium needs, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications that can affect potassium levels.
7. What Happens If I Don’t Get Enough Potassium?
Potassium deficiency, also known as hypokalemia, can lead to various health issues. Recognizing the symptoms of low potassium levels is crucial for addressing the deficiency promptly.
- Muscle Weakness and Cramps: One of the most common symptoms of potassium deficiency is muscle weakness and cramps. Potassium plays a vital role in muscle contractions, and low levels can impair muscle function.
- Fatigue: Potassium deficiency can cause fatigue and general weakness. Low potassium levels can affect energy production in the body.
- Irregular Heartbeat: Potassium is essential for maintaining a regular heartbeat. Low levels can lead to arrhythmias, which can be dangerous.
- Constipation: Potassium helps regulate digestive function. Deficiency can lead to constipation and other digestive issues.
- High Blood Pressure: Potassium helps regulate blood pressure, and low levels can contribute to high blood pressure.
- Numbness and Tingling: Potassium deficiency can affect nerve function, leading to numbness and tingling in the extremities.
If you suspect you have a potassium deficiency, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Treatment typically involves increasing potassium intake through diet or supplements.
8. Are There Any Risks Associated With Too Much Potassium?
While potassium is essential, consuming too much can also lead to health problems. Hyperkalemia, or high potassium levels, can be a serious condition, especially for individuals with kidney issues.
- Heart Problems: High potassium levels can cause arrhythmias and other heart problems. In severe cases, hyperkalemia can lead to cardiac arrest.
- Muscle Weakness: Although low potassium can cause muscle weakness, so can high potassium levels.
- Numbness and Tingling: Similar to potassium deficiency, high potassium levels can also cause numbness and tingling in the extremities.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Hyperkalemia can lead to gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Individuals with kidney disease, diabetes, or those taking certain medications are at a higher risk of developing hyperkalemia. It’s essential to monitor potassium levels and follow medical advice to avoid excessive intake.
9. How Can I Incorporate Potassium Rich Foods Into My Diet?
Incorporating potassium rich foods into your diet is easy and delicious. Here are some practical tips to help you increase your potassium intake:
- Start with Breakfast: Add bananas, berries, or yogurt to your breakfast routine. These foods are a great way to kickstart your potassium intake for the day.
- Snack Smart: Choose potassium-rich snacks like almonds, dried apricots, or a small sweet potato.
- Include Vegetables in Every Meal: Make sure to include potassium-rich vegetables like spinach, tomatoes, or Brussels sprouts in your lunch and dinner.
- Use Potassium-Rich Cooking Methods: Steaming or baking vegetables can help retain more potassium compared to boiling.
- Add Legumes to Your Diet: Incorporate beans and lentils into soups, stews, and salads for a potassium boost.
- Drink Potassium-Rich Beverages: Orange juice and milk are good sources of potassium and can be easily added to your daily routine.
- Read Food Labels: Check food labels for potassium content and choose foods that are higher in potassium.
- Plan Your Meals: Plan your meals around potassium-rich foods to ensure you are meeting your daily requirements.
10. Can Potassium Supplements Help?
Potassium supplements are available, but they should only be taken under medical supervision. It’s generally better to obtain potassium from food sources, as supplements can sometimes lead to excessive intake and potential health risks.
If you are considering potassium supplements, consult with a healthcare professional to determine if they are necessary and to ensure you are taking a safe dosage. Individuals with kidney problems or those taking certain medications should be particularly cautious with potassium supplements.
11. What Are Some Delicious Potassium Rich Recipes?
To help you incorporate more potassium rich foods into your diet, here are a few delicious and easy recipes:
11.1. Sweet Potato and Black Bean Tacos
These tacos are packed with potassium, fiber, and flavor.
Ingredients:
- 2 medium sweet potatoes, peeled and diced
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- 1 onion, chopped
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 teaspoon chili powder
- 1/2 teaspoon cumin
- 1/4 teaspoon cayenne pepper (optional)
- 1 can (15 ounces) black beans, rinsed and drained
- 1/2 cup corn kernels
- 1/4 cup chopped cilantro
- 1 tablespoon lime juice
- Salt and pepper to taste
- Tortillas, for serving
- Optional toppings: avocado, salsa, sour cream
Instructions:
- Preheat oven to 400°F (200°C). Toss sweet potatoes with olive oil, salt, and pepper. Spread on a baking sheet and roast for 20-25 minutes, or until tender.
- While sweet potatoes are roasting, sauté onion and garlic in a skillet until softened. Add chili powder, cumin, and cayenne pepper (if using), and cook for 1 minute.
- Stir in black beans, corn, cilantro, and lime juice. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
- Warm tortillas according to package directions. Fill each tortilla with roasted sweet potatoes and black bean mixture.
- Top with your favorite toppings and enjoy.
11.2. Spinach and Banana Smoothie
This smoothie is a quick and easy way to boost your potassium and nutrient intake.
Ingredients:
- 1 banana
- 1 cup spinach
- 1/2 cup yogurt
- 1/2 cup milk
- 1 tablespoon almond butter
- 1 teaspoon honey (optional)
Instructions:
- Combine all ingredients in a blender.
- Blend until smooth.
- Add more milk if needed to reach desired consistency.
- Enjoy immediately.
11.3. Baked Salmon with Roasted Brussels Sprouts
This recipe is a healthy and delicious way to get your potassium and omega-3 fatty acids.
Ingredients:
- 2 salmon fillets
- 1 pound Brussels sprouts, trimmed and halved
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- 1 lemon, sliced
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- Preheat oven to 400°F (200°C).
- Toss Brussels sprouts with olive oil, salt, and pepper. Spread on a baking sheet.
- Place salmon fillets on a separate baking sheet lined with parchment paper. Top with lemon slices, salt, and pepper.
- Bake salmon and Brussels sprouts for 12-15 minutes, or until salmon is cooked through and Brussels sprouts are tender.
- Serve immediately.
12. How Does Potassium Interact With Other Nutrients In The Body?
Potassium interacts with other nutrients in the body, influencing various physiological processes. Understanding these interactions can help you optimize your diet for overall health.
- Sodium: Potassium and sodium work together to maintain fluid balance and regulate blood pressure. A high sodium intake can deplete potassium levels, and vice versa.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is essential for potassium absorption and utilization. Low magnesium levels can impair potassium transport into cells.
- Calcium: Potassium and calcium work together to support bone health. Adequate potassium intake can help reduce calcium excretion in the urine.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a role in potassium regulation. Vitamin D deficiency can affect potassium levels in the body.
13. What Are Some Common Myths About Potassium Rich Foods?
There are several common myths about potassium rich foods that can lead to confusion and misinformation. It’s essential to debunk these myths to make informed dietary choices.
- Myth: Bananas Are the Only Good Source of Potassium: While bananas are a well-known source of potassium, many other fruits, vegetables, and foods contain even higher amounts of this mineral.
- Myth: You Can Get Enough Potassium from Supplements Alone: While supplements can help, it’s generally better to obtain potassium from food sources. Supplements may not be as easily absorbed and can lead to excessive intake.
- Myth: High Potassium Intake Is Always Safe: While potassium is essential, consuming too much can be dangerous, especially for individuals with kidney problems.
- Myth: Only Athletes Need to Worry About Potassium Intake: Potassium is essential for everyone, not just athletes. It plays a vital role in various bodily functions, regardless of activity level.
- Myth: Cooking Always Destroys Potassium in Foods: While some potassium can be lost during cooking, many cooking methods, such as steaming and baking, help retain more potassium compared to boiling.
14. Can Certain Medications Affect Potassium Levels?
Yes, certain medications can affect potassium levels in the body. It’s essential to be aware of these interactions and consult with a healthcare professional if you are taking any medications that may affect your potassium levels.
- Diuretics: Some diuretics, also known as water pills, can cause potassium loss through increased urination.
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: These medications, commonly used to treat high blood pressure, can increase potassium levels.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can sometimes increase potassium levels, especially in individuals with kidney problems.
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretics: These diuretics, such as spironolactone, can increase potassium levels.
If you are taking any of these medications, your healthcare provider may recommend regular monitoring of your potassium levels to ensure they remain within a healthy range.
15. How Does Potassium Intake Vary Across Different Cultures?
Potassium intake can vary significantly across different cultures due to variations in dietary patterns and food availability. Understanding these differences can provide insights into how different populations meet their potassium needs.
- Western Diets: Western diets, often characterized by high sodium and processed foods, tend to be lower in potassium.
- Mediterranean Diets: Mediterranean diets, rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, are typically higher in potassium.
- Asian Diets: Asian diets, which often include a variety of vegetables, fruits, and legumes, can be good sources of potassium, although sodium intake may also be high.
- Vegetarian and Vegan Diets: Vegetarian and vegan diets, which emphasize plant-based foods, are generally higher in potassium compared to diets that include meat.
Cultural dietary habits can significantly impact potassium intake, highlighting the importance of promoting balanced diets rich in potassium-rich foods.
16. What Are Some Tips For Maintaining Healthy Potassium Levels?
Maintaining healthy potassium levels involves a combination of dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and awareness of potential risk factors. Here are some tips to help you keep your potassium levels in a healthy range:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming a variety of potassium rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products.
- Limit Sodium Intake: High sodium intake can deplete potassium levels. Reduce your intake of processed foods and limit your use of table salt.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for maintaining fluid balance and potassium levels. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Monitor Potassium Levels: If you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications that can affect potassium levels, monitor your levels regularly as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can affect potassium levels and overall health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormone levels and potassium balance. Practice stress-management techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: If you have any concerns about your potassium levels or are experiencing symptoms of deficiency or excess, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
17. How Can I Track My Potassium Intake?
Tracking your potassium intake can help you ensure you are meeting your daily requirements. There are several methods you can use to monitor your potassium consumption:
- Food Diaries: Keep a food diary to record everything you eat and drink. Use online databases or nutrition labels to estimate the potassium content of each food.
- Nutrition Tracking Apps: Use nutrition tracking apps like MyFitnessPal or Cronometer to log your meals and track your potassium intake automatically.
- Consult with a Registered Dietitian: A registered dietitian can help you assess your dietary habits and provide personalized recommendations for meeting your potassium needs.
- Review Food Labels: Check food labels for potassium content and keep a record of the potassium values of the foods you consume regularly.
By tracking your potassium intake, you can identify areas where you may need to make dietary adjustments to ensure you are getting enough of this essential mineral.
18. What Is The Role Of Potassium In Athletic Performance?
Potassium plays a crucial role in athletic performance, influencing muscle function, hydration, and overall energy levels. Adequate potassium intake is essential for athletes to optimize their performance and prevent muscle cramps.
- Muscle Function: Potassium is essential for muscle contractions, and low levels can impair muscle function and lead to muscle weakness and cramps.
- Hydration: Potassium helps maintain fluid balance, which is crucial for hydration during exercise. Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances and decreased performance.
- Nerve Function: Potassium plays a role in transmitting nerve signals, which are essential for muscle coordination and reaction time.
- Energy Production: Potassium is involved in energy production in the body. Low levels can lead to fatigue and decreased endurance.
Athletes should focus on consuming potassium rich foods as part of a balanced diet to support their performance and prevent potassium deficiency.
19. How Does Potassium Affect Blood Pressure?
Potassium plays a significant role in regulating blood pressure, helping to balance out the effects of sodium in the body. Adequate potassium intake can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Sodium Balance: Potassium helps regulate blood pressure by balancing out the effects of sodium. High sodium intake can increase blood pressure, while adequate potassium intake can help lower it.
- Blood Vessel Relaxation: Potassium helps relax blood vessels, which can lower blood pressure.
- Kidney Function: Potassium helps regulate kidney function, which plays a role in blood pressure control.
Individuals with high blood pressure should focus on increasing their potassium intake through diet and limiting their sodium intake to help manage their blood pressure levels.
20. What Are Some Kid-Friendly Potassium Rich Foods?
Ensuring children get enough potassium is essential for their growth and development. Here are some kid-friendly potassium rich foods that are easy to incorporate into their diet:
- Bananas: A classic and convenient snack that kids love.
- Sweet Potatoes: Roasted sweet potato fries are a healthy and delicious option.
- Yogurt: A good source of potassium and calcium, yogurt can be enjoyed as a snack or part of a meal.
- Oranges: A refreshing and vitamin C-rich fruit that kids enjoy.
- Avocados: Creamy and mild-flavored, avocados can be added to sandwiches or dips.
- Milk: A good source of potassium and calcium, milk is an essential part of a child’s diet.
- Beans: Beans can be added to soups, stews, or dips for a potassium boost.
- Dried Fruits: Dried apricots and raisins are a sweet and potassium-rich treat.
By offering a variety of kid-friendly potassium rich foods, you can help ensure your children are meeting their daily potassium needs.
21. Where Can I Find More Information About Potassium Rich Foods And Recipes?
For more information about potassium rich foods and recipes, larosafoods.com is your go-to resource. We offer a wide range of articles, recipes, and tips to help you incorporate potassium rich foods into your diet and improve your overall health.
- Website: Visit larosafoods.com for a comprehensive collection of articles, recipes, and resources on potassium rich foods.
- Address: 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States.
- Phone: +1 (415) 987-0123.
Whether you’re looking for new recipes, nutritional information, or expert advice, larosafoods.com has everything you need to make informed dietary choices and prioritize your health.
FAQ About Potassium Rich Foods
1. What are the signs of potassium deficiency?
Muscle weakness, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and constipation are common signs.
2. Can too much potassium be harmful?
Yes, it can lead to heart problems and muscle weakness, especially in individuals with kidney issues.
3. How can I increase my potassium intake?
Incorporate potassium rich foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach into your diet.
4. Are potassium supplements necessary?
Only under medical supervision, as it’s better to obtain potassium from food sources.
5. How much potassium do I need daily?
Adults need around 4,700 mg of potassium per day.
6. Can certain medications affect potassium levels?
Yes, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and NSAIDs can affect potassium levels.
7. What are some kid-friendly potassium rich foods?
Bananas, sweet potatoes, yogurt, and oranges are great options for kids.
8. How does potassium affect blood pressure?
Potassium helps regulate blood pressure by balancing out the effects of sodium.
9. Is it safe to consume potassium rich foods during pregnancy?
Yes, pregnant women need 4,700 mg of potassium daily and can obtain it through a balanced diet.
10. How does cooking affect the potassium content of foods?
Some potassium can be lost during cooking, but steaming and baking help retain more potassium compared to boiling.
Ready to explore a world of potassium-packed recipes and expert nutritional advice? Visit larosafoods.com now and start your journey towards a healthier, more vibrant you. Discover delicious ways to boost your potassium intake, master essential cooking techniques, and unlock the secrets to a balanced, nutritious diet. Your culinary adventure awaits!


