Food Production significantly impacts our carbon footprint, and larosafoods.com is here to explore this vital intersection of food and environmental sustainability. By understanding the environmental impact of various food choices and production methods, we can all make more informed decisions for a healthier planet. Join us as we uncover the surprising truths about sustainable eating, eco-friendly food choices, and the role of innovative food production in creating a greener future, ensuring we offer resources and recipes that align with sustainable diets and mindful meal planning.
1. What Is The Carbon Footprint Of Food Production?
The carbon footprint of food production is the total greenhouse gas emissions generated by producing, processing, transporting, storing, and disposing of food. A study from the University of Oxford, published in Science in 2018, found that food production accounts for 26% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding this footprint helps us make informed food choices.
1.1 What Factors Contribute To The Carbon Footprint of Food?
Several factors contribute to the carbon footprint of food.
- Land Use: Deforestation and land conversion for agriculture release significant amounts of carbon dioxide.
- On-Farm Emissions: Livestock farming emits methane and nitrous oxide, potent greenhouse gases.
- Production of Agricultural Inputs: Manufacturing fertilizers and pesticides requires energy and releases emissions.
- Food Processing: Processing plants consume energy and produce waste.
- Transportation: Moving food from farms to consumers involves fuel consumption and emissions.
- Packaging: Producing and disposing of food packaging contributes to emissions.
- Retail: Supermarkets and grocery stores use energy for refrigeration and lighting.
- Waste: Food waste decomposes and releases methane in landfills.
1.2 Why Is It Important to Understand the Carbon Footprint of Food Production?
Understanding the carbon footprint of food production is crucial for several reasons.
- Environmental Impact: It helps us assess the environmental consequences of our food choices.
- Informed Decisions: It empowers consumers to make more sustainable dietary choices.
- Policy Development: It informs policymakers in developing strategies to reduce emissions from the food sector.
- Innovation: It encourages innovation in food production methods to lower carbon footprints.
- Sustainability: It promotes sustainable agricultural practices that minimize environmental harm.
2. What Role Does Transportation Play In Food’s Carbon Footprint?
Transportation typically accounts for a small portion, around 5%, of a food’s total carbon footprint. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the majority of emissions come from land use change and on-farm activities. This challenges the common belief that eating locally is always the most sustainable option.
2.1 How Does Food Transportation Contribute to Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
Food transportation contributes to greenhouse gas emissions through the burning of fossil fuels in trucks, ships, and airplanes. The amount of emissions depends on the distance traveled, the mode of transport, and the type of food being transported. Despite this, transport is often a smaller factor compared to production methods.
2.2 Which Transportation Methods Are Most and Least Carbon-Intensive?
The carbon intensity of different transportation methods varies significantly.
| Transportation Method | Carbon Intensity (CO2eq per tonne kilometer) |
|---|---|
| Air Freight | High (approximately 50 times more than boat) |
| Trucking | Moderate |
| Shipping by Boat | Low |
As the table indicates, shipping by boat is the most carbon-efficient method for transporting food over long distances. Air freight, while faster, has a significantly higher carbon footprint.
2.3 Should I Always Prioritize Locally Sourced Food To Reduce Transportation Emissions?
Prioritizing locally sourced food doesn’t always guarantee a lower carbon footprint. What you eat matters more than where it comes from. For example, locally produced beef can have a much higher carbon footprint than peas shipped from another continent. This is because the production of beef involves significant land use and methane emissions, which outweigh the transportation emissions.
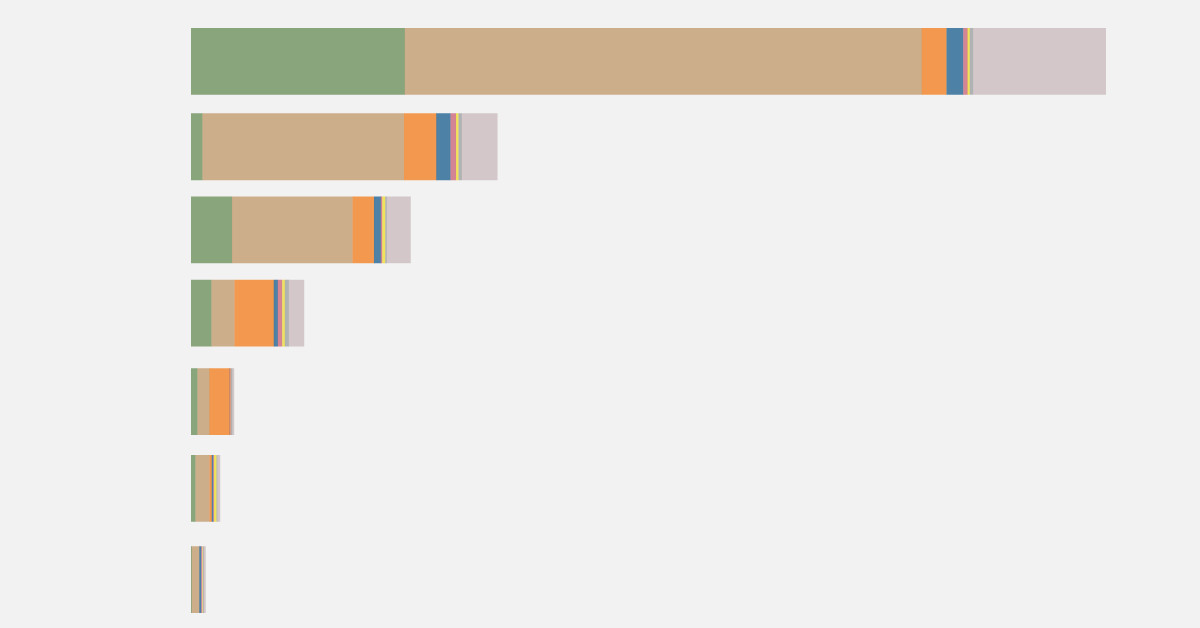 Locally-produced foods carbon footprint
Locally-produced foods carbon footprint
3. Which Types of Food Have The Highest Carbon Footprint?
Animal products, particularly beef, generally have the highest carbon footprint. Producing one kilogram of beef emits about 60 kilograms of greenhouse gases. In contrast, plant-based foods like peas have a much lower footprint, emitting only about 1 kilogram of greenhouse gases per kilogram.
3.1 What Makes Animal Products More Carbon-Intensive Than Plant-Based Foods?
Animal products are more carbon-intensive for several reasons.
- Land Use: Raising livestock requires large areas of land for grazing and growing feed crops, leading to deforestation and habitat loss.
- Methane Emissions: Ruminant animals like cows produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas, during digestion.
- Feed Production: Producing animal feed requires energy and resources, contributing to emissions.
- Manure Management: Manure releases nitrous oxide, another significant greenhouse gas.
- Inefficiency: Converting plant-based feed into animal protein is less efficient than direct consumption of plants.
3.2 Can Sustainable Farming Practices Reduce The Carbon Footprint Of Animal Products?
Yes, sustainable farming practices can reduce the carbon footprint of animal products. Some strategies include:
- Improved Grazing Management: Implementing rotational grazing and optimizing pasture management can enhance carbon sequestration in soils.
- Feed Optimization: Using more efficient and sustainable feed sources can reduce emissions from feed production.
- Manure Management Techniques: Anaerobic digestion and other manure management techniques can capture methane for energy production.
- Precision Livestock Farming: Using technology to monitor and manage livestock can improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into livestock farming systems can sequester carbon and provide additional benefits.
3.3 What Are Some Low-Carbon Food Choices?
Choosing low-carbon foods can significantly reduce your environmental impact. Here are some options:
- Plant-Based Proteins: Legumes, tofu, and nuts have a much lower carbon footprint than animal products.
- Vegetables and Fruits: Seasonal and locally grown produce reduces transportation emissions and supports local farmers.
- Grains: Whole grains like rice, wheat, and oats have a relatively low carbon footprint.
- Sustainable Seafood: Choosing seafood from well-managed fisheries can minimize environmental impact.
- Dairy Alternatives: Plant-based milk alternatives like almond, soy, and oat milk generally have lower emissions than dairy milk.
4. How Does Food Waste Contribute To Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
Food waste is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. According to the EPA, food waste in landfills is the third largest source of methane emissions in the United States. Reducing food waste can have a substantial impact on lowering our carbon footprint.
4.1 What Happens When Food Waste Decomposes in Landfills?
When food waste decomposes in landfills, it undergoes anaerobic digestion, producing methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Methane has a global warming potential that is 25 times higher than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. This means that even small amounts of food waste can have a significant impact on climate change.
4.2 What Steps Can Be Taken To Reduce Food Waste At Home?
Several steps can be taken to reduce food waste at home:
- Plan Meals: Plan your meals ahead of time and create a shopping list to avoid buying unnecessary items.
- Proper Storage: Store food properly to extend its shelf life.
- Use Leftovers: Get creative with leftovers and incorporate them into new meals.
- Composting: Compost food scraps to create nutrient-rich soil for your garden.
- Buy Only What You Need: Avoid buying in bulk unless you are sure you can use the food before it spoils.
- Understand Expiration Dates: Use “best by” and “use by” dates as guidelines rather than strict rules.
4.3 How Can Businesses Reduce Food Waste?
Businesses can also take steps to reduce food waste:
- Inventory Management: Implement effective inventory management systems to track and minimize food spoilage.
- Donation Programs: Donate excess food to local food banks and shelters.
- Employee Training: Train employees on proper food handling and waste reduction techniques.
- Composting Programs: Implement composting programs to divert food waste from landfills.
- Menu Optimization: Design menus that utilize ingredients efficiently and minimize waste.
5. What Is Sustainable Agriculture And How Does It Affect Food Production?
Sustainable agriculture refers to farming practices that meet current food and textile needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It focuses on environmental health, economic profitability, and social and economic equity. Sustainable agriculture can significantly reduce the environmental impact of food production.
5.1 What Are The Key Principles Of Sustainable Agriculture?
The key principles of sustainable agriculture include:
- Soil Health: Maintaining and improving soil health through practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage.
- Water Conservation: Using water efficiently through irrigation techniques and water harvesting.
- Biodiversity: Promoting biodiversity by maintaining diverse ecosystems and habitats on farms.
- Integrated Pest Management: Using integrated pest management strategies to minimize pesticide use.
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through the use of renewable energy and efficient farming practices.
5.2 How Can Farmers Implement Sustainable Practices?
Farmers can implement sustainable practices in various ways:
- Crop Rotation: Rotating crops can improve soil health, reduce pest and disease pressure, and increase yields.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops can prevent soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and suppress weeds.
- Reduced Tillage: Minimizing tillage can reduce soil erosion, conserve soil moisture, and improve soil structure.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM involves using a combination of biological, cultural, and chemical methods to control pests.
- Water Management: Implementing efficient irrigation systems and water harvesting techniques can conserve water.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into farming systems can provide shade, reduce erosion, and sequester carbon.
5.3 What Are The Benefits Of Sustainable Agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture offers numerous benefits:
- Environmental Protection: Reduces pollution, conserves resources, and protects biodiversity.
- Economic Viability: Increases long-term profitability and reduces reliance on external inputs.
- Social Equity: Promotes fair labor practices and supports local communities.
- Food Security: Enhances food production and resilience to climate change.
- Health Benefits: Produces healthier food and reduces exposure to harmful chemicals.
6. How Can Technology Improve Food Production Sustainability?
Technology plays a crucial role in improving food production sustainability. Innovations like precision agriculture, vertical farming, and alternative protein sources can reduce the environmental impact of food production.
6.1 What Is Precision Agriculture and How Does It Help?
Precision agriculture involves using technology to monitor and manage crops and livestock more efficiently. This includes:
- GPS Technology: Using GPS to map fields and apply inputs (fertilizers, pesticides, water) only where needed.
- Sensors: Using sensors to monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop health.
- Drones: Using drones to survey fields and identify areas of stress or pest infestation.
- Data Analytics: Using data analytics to optimize farming practices and improve yields.
6.2 What Are The Advantages of Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often indoors. Advantages include:
- Increased Yields: Higher yields per square foot compared to traditional farming.
- Reduced Water Use: Recirculating water systems reduce water consumption.
- Pest and Disease Control: Controlled environments reduce the need for pesticides.
- Year-Round Production: Crops can be grown year-round regardless of weather conditions.
- Reduced Transportation: Vertical farms can be located in urban areas, reducing transportation emissions.
6.3 What Is The Potential of Alternative Protein Sources?
Alternative protein sources like plant-based proteins, cultured meat, and insect-based proteins offer the potential to reduce the environmental impact of protein production.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Producing plant-based proteins like legumes, tofu, and tempeh requires less land, water, and energy compared to animal agriculture.
- Cultured Meat: Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown meat, is produced by culturing animal cells in a lab. It has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and land use.
- Insect-Based Proteins: Insects are a sustainable source of protein that require less land, water, and feed compared to traditional livestock.
7. How Do Government Policies Influence Sustainable Food Production?
Government policies play a critical role in promoting sustainable food production. Policies can incentivize sustainable practices, regulate harmful activities, and support research and development in sustainable agriculture.
7.1 What Types of Policies Support Sustainable Agriculture?
Several types of policies can support sustainable agriculture:
- Subsidies: Providing subsidies for farmers who adopt sustainable practices like cover cropping and reduced tillage.
- Regulations: Implementing regulations to reduce pollution from agricultural activities.
- Research and Development: Funding research and development in sustainable agriculture technologies and practices.
- Education and Outreach: Providing education and outreach programs to help farmers adopt sustainable practices.
- Certification Programs: Supporting certification programs that promote sustainable agriculture practices.
7.2 How Can Consumers Advocate For Sustainable Food Policies?
Consumers can advocate for sustainable food policies by:
- Supporting Businesses: Supporting businesses that prioritize sustainability and advocate for policy changes.
- Contacting Representatives: Contacting elected officials to express support for sustainable food policies.
- Joining Advocacy Groups: Joining advocacy groups that work to promote sustainable food systems.
- Educating Others: Educating friends, family, and community members about sustainable food issues and policies.
7.3 What Are Some Examples Of Successful Sustainable Food Policies?
Examples of successful sustainable food policies include:
- Organic Certification Programs: These programs provide standards and certification for organic farming practices, promoting environmental sustainability and consumer trust.
- Conservation Easements: These agreements protect agricultural land from development, preserving valuable farmland and ecosystems.
- Farm-to-School Programs: These programs connect schools with local farms, providing students with healthy, locally sourced meals and supporting local farmers.
8. What Role Do Consumers Play In Promoting Sustainable Food Production?
Consumers play a vital role in promoting sustainable food production through their purchasing decisions, dietary choices, and waste reduction efforts. By making informed choices, consumers can drive demand for sustainable products and practices.
8.1 How Can Consumers Make More Sustainable Food Choices?
Consumers can make more sustainable food choices by:
- Choosing Plant-Based Foods: Reducing consumption of animal products and increasing consumption of plant-based foods.
- Buying Local and Seasonal: Buying locally sourced and seasonal produce to reduce transportation emissions.
- Reducing Food Waste: Planning meals, storing food properly, and using leftovers to minimize food waste.
- Choosing Sustainable Seafood: Selecting seafood from well-managed fisheries and avoiding overfished species.
- Supporting Sustainable Brands: Buying from brands that prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing.
8.2 Why Is It Important To Support Local Farmers?
Supporting local farmers is important for several reasons:
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces transportation emissions and supports sustainable farming practices.
- Economic Benefits: Supports local economies and creates jobs.
- Social Benefits: Strengthens communities and provides access to fresh, healthy food.
- Transparency: Provides greater transparency about where your food comes from and how it is produced.
8.3 How Can I Identify Products That Are Produced Sustainably?
You can identify products that are produced sustainably by looking for certifications and labels such as:
- Organic Certification: Indicates that the product was produced using organic farming practices.
- Fair Trade Certification: Indicates that the product was produced using fair labor practices.
- Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) Certification: Indicates that the seafood product comes from a sustainable fishery.
- Rainforest Alliance Certification: Indicates that the product was produced using sustainable farming practices that protect biodiversity.
9. How Does Climate Change Impact Food Production?
Climate change is already impacting food production through changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. These changes can reduce crop yields, disrupt supply chains, and increase food prices.
9.1 What Are The Specific Impacts Of Climate Change On Agriculture?
Specific impacts of climate change on agriculture include:
- Reduced Crop Yields: Higher temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns can reduce crop yields.
- Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: Climate change can create conditions that favor the spread of pests and diseases.
- Water Scarcity: Changes in precipitation patterns can lead to water scarcity in some regions, making it difficult to grow crops.
- Extreme Weather Events: Extreme weather events like droughts, floods, and heatwaves can damage crops and disrupt supply chains.
- Soil Degradation: Climate change can exacerbate soil degradation, reducing soil fertility and productivity.
9.2 How Can Food Production Adapt To Climate Change?
Food production can adapt to climate change through:
- Developing Climate-Resilient Crops: Breeding crops that are more tolerant to drought, heat, and pests.
- Improving Water Management: Implementing efficient irrigation systems and water harvesting techniques.
- Adopting Sustainable Farming Practices: Using sustainable farming practices that improve soil health and reduce emissions.
- Diversifying Crop Production: Growing a variety of crops to reduce vulnerability to climate change impacts.
- Investing in Research and Development: Investing in research and development to develop new technologies and practices for climate-resilient agriculture.
9.3 What Are The Long-Term Consequences If We Fail To Address Climate Change Impacts On Food Production?
If we fail to address climate change impacts on food production, we can expect to see:
- Food Shortages: Reduced crop yields and disruptions to supply chains can lead to food shortages.
- Increased Food Prices: Food shortages can drive up food prices, making it difficult for people to afford healthy food.
- Malnutrition: Food shortages and increased food prices can lead to malnutrition, particularly in vulnerable populations.
- Social Unrest: Food shortages and economic hardship can lead to social unrest and political instability.
- Environmental Degradation: Desperate attempts to increase food production can lead to further environmental degradation.
10. What Innovations Are Shaping The Future Of Food Production?
Several innovations are shaping the future of food production, including cellular agriculture, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology. These innovations have the potential to transform the way we produce, distribute, and consume food.
10.1 What Is Cellular Agriculture And Its Potential?
Cellular agriculture involves producing food directly from cells, rather than from whole plants or animals. This includes:
- Cultured Meat: Producing meat by culturing animal cells in a lab.
- Precision Fermentation: Using microorganisms to produce ingredients like proteins and fats.
Cellular agriculture has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of food production, as it requires less land, water, and energy compared to traditional agriculture.
10.2 How Can Artificial Intelligence (AI) Improve Food Production?
Artificial intelligence (AI) can improve food production by:
- Optimizing Crop Management: Using AI to analyze data from sensors and drones to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- Predicting Yields: Using AI to predict crop yields and inform planting and harvesting decisions.
- Improving Supply Chain Efficiency: Using AI to optimize logistics and reduce food waste in the supply chain.
- Developing New Crop Varieties: Using AI to accelerate the breeding of new crop varieties that are more resilient to climate change.
10.3 What Is The Role Of Blockchain In Food Traceability?
Blockchain technology can improve food traceability by creating a transparent and secure record of the entire food supply chain. This allows consumers to track the journey of their food from farm to table, ensuring food safety and authenticity.
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent record of all transactions in the food supply chain.
- Improved Food Safety: Blockchain allows for rapid identification and tracing of contaminated food products.
- Enhanced Authenticity: Blockchain can verify the authenticity of food products, preventing fraud and counterfeiting.
- Greater Consumer Trust: Blockchain can build consumer trust by providing verifiable information about the origin and production of their food.
Ready to explore sustainable recipes, discover eco-friendly cooking tips, and learn more about the future of food? Visit larosafoods.com today and join our community of food enthusiasts dedicated to making a positive impact on the planet. Contact us at Address: 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States, Phone: +1 (415) 987-0123, or visit our website at larosafoods.com.
FAQ About Food Production
1. Is Eating Locally Always Better for the Environment?
Not always. While reducing transportation emissions is beneficial, the production method of the food often has a greater impact. For example, locally produced beef can have a higher carbon footprint than imported vegetables due to the emissions associated with raising livestock.
2. What Foods Have the Lowest Carbon Footprint?
Plant-based foods like legumes, vegetables, fruits, and grains generally have the lowest carbon footprints. These foods require less land, water, and energy to produce compared to animal products.
3. How Does Food Waste Contribute to Climate Change?
Food waste in landfills decomposes and produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Reducing food waste can significantly lower your carbon footprint.
4. What is Sustainable Agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture refers to farming practices that meet current food needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It focuses on environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity.
5. How Can I Reduce My Carbon Footprint Through My Food Choices?
You can reduce your carbon footprint by eating more plant-based foods, buying local and seasonal produce, reducing food waste, and choosing sustainable seafood.
6. What Role Does Technology Play in Sustainable Food Production?
Technology like precision agriculture, vertical farming, and alternative protein sources can improve food production sustainability by increasing efficiency, reducing resource use, and minimizing environmental impact.
7. How Do Government Policies Support Sustainable Food Production?
Government policies can incentivize sustainable practices, regulate harmful activities, and support research and development in sustainable agriculture.
8. What is Cellular Agriculture?
Cellular agriculture involves producing food directly from cells, rather than from whole plants or animals. This includes cultured meat and precision fermentation.
9. How Can AI Improve Food Production?
Artificial intelligence (AI) can improve food production by optimizing crop management, predicting yields, improving supply chain efficiency, and developing new crop varieties.
10. What is the Role of Blockchain in Food Traceability?
Blockchain technology can improve food traceability by creating a transparent and secure record of the entire food supply chain, ensuring food safety and authenticity.

