What Foods Have High Potassium? Discover the powerhouse foods packed with potassium, essential for maintaining optimal health, especially for culinary enthusiasts in the USA, at larosafoods.com.
Potassium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, from muscle contractions to nerve signaling. Including potassium-rich foods in your diet is not only beneficial for your overall health but also enhances your culinary creations. At larosafoods.com, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive guide to incorporating these foods into your daily meals, ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet. Explore our extensive collection of recipes and nutritional information to make the most of potassium-rich ingredients.
1. Why Is Potassium Important?
Why is potassium so essential for our well-being? Potassium is crucial for maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions in the body, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It helps regulate heartbeat, ensures proper nerve signaling, and assists in moving nutrients into cells and waste products out.
Potassium is an electrolyte, which means it carries an electric charge when dissolved in body fluids such as blood. This electrical charge is critical for the function of nerves and muscles, including the heart. Maintaining the right balance of potassium is essential for overall health, as imbalances can lead to various health issues.
1.1. The Role of Potassium in the Body
What specific roles does potassium play in maintaining bodily functions? Potassium’s main roles include regulating blood pressure, supporting nerve transmission, and enabling muscle contractions, according to a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. These functions are vital for everyday activities and long-term health.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Potassium helps to balance the effects of sodium in the body, which can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels. This is particularly important for individuals with hypertension.
- Nerve Transmission: Potassium ions are essential for transmitting nerve signals throughout the body. These signals allow for communication between the brain and other parts of the body, enabling movement and sensation.
- Muscle Contraction: Potassium plays a key role in muscle contractions, including those of the heart. Proper potassium levels ensure that muscles contract efficiently and effectively.
1.2. Health Benefits of Potassium
How does sufficient potassium intake benefit our health? Adequate potassium intake can lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of stroke, and support bone health, according to Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Additionally, it aids in preventing kidney stones and maintaining proper muscle function.
- Lower Blood Pressure: Studies have shown that increasing potassium intake can help lower blood pressure, especially in individuals with hypertension. This is because potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium, which can raise blood pressure.
- Reduced Risk of Stroke: Potassium can reduce the risk of stroke by helping to maintain healthy blood pressure levels and supporting overall cardiovascular health.
- Bone Health: Some research suggests that potassium can help maintain bone density and prevent osteoporosis, particularly in older adults.
- Prevention of Kidney Stones: Potassium can help prevent the formation of kidney stones by reducing the amount of calcium excreted in the urine.
- Proper Muscle Function: Potassium is crucial for maintaining muscle strength and preventing muscle cramps, especially during exercise.
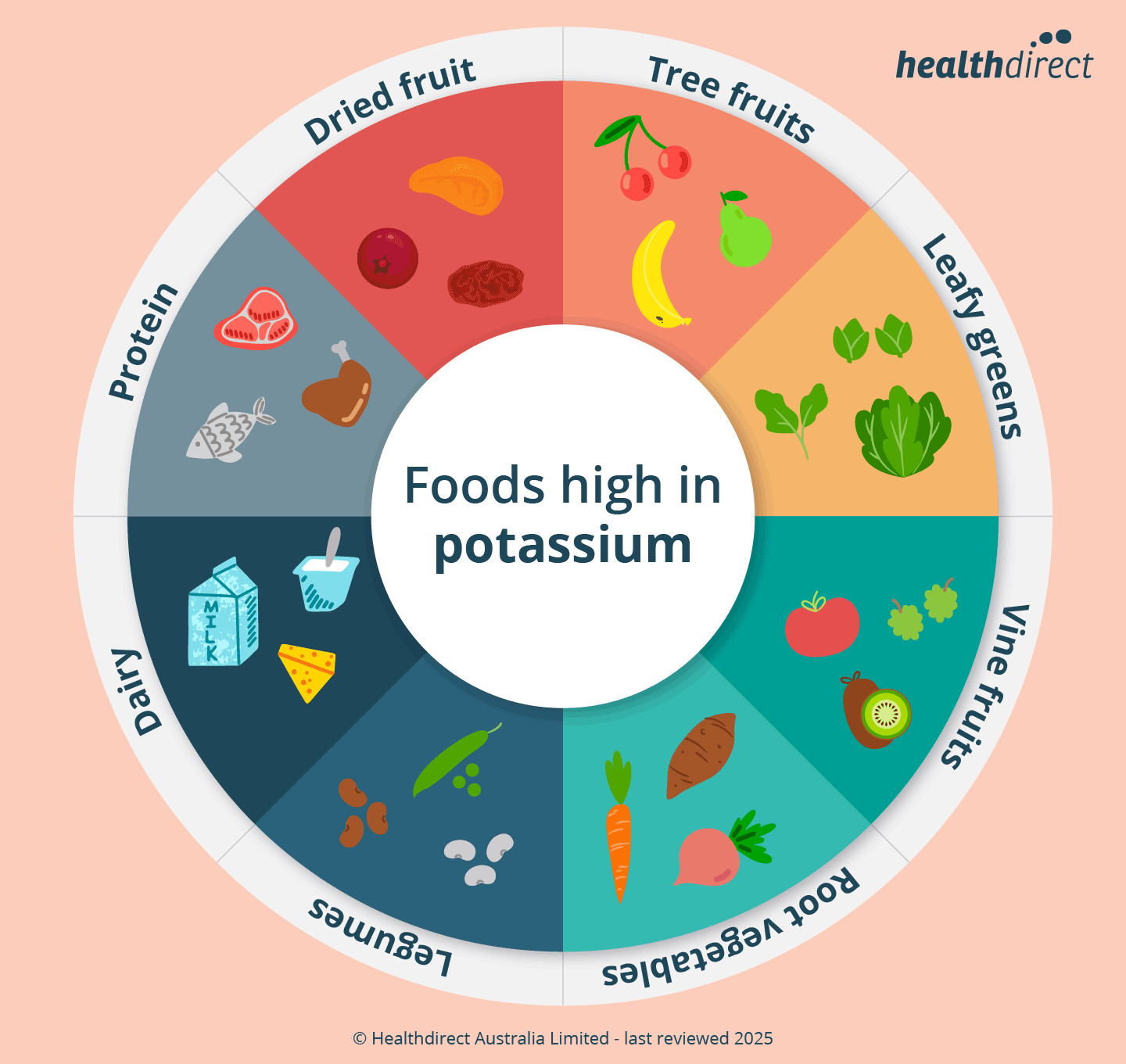
2. Top Foods High in Potassium
What are the top food sources of potassium that you should include in your diet? The best sources of potassium include bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, beans, and avocados, according to the USDA National Nutrient Database. These foods offer a variety of ways to boost your potassium intake through delicious and nutritious meals.
Incorporating these foods into your regular diet can significantly improve your potassium levels and contribute to overall health. Whether you prefer fruits, vegetables, or legumes, there are plenty of options to choose from.
2.1. Fruits Rich in Potassium
Which fruits are exceptionally high in potassium? Bananas are well-known, but kiwis, apricots, and cantaloupe are also excellent sources of potassium, as noted by the Mayo Clinic. These fruits can be easily added to breakfasts, snacks, or desserts for a potassium boost.
- Bananas: A medium-sized banana contains about 422 mg of potassium, making it a convenient and tasty source.
- Kiwis: One kiwi provides around 215 mg of potassium and is also packed with vitamin C and other nutrients.
- Apricots: Fresh apricots offer about 259 mg of potassium per cup, while dried apricots provide an even more concentrated source.
- Cantaloupe: This melon contains approximately 427 mg of potassium per cup and is a refreshing and hydrating option.
2.2. Vegetables High in Potassium
What vegetables are great sources of potassium? Sweet potatoes, spinach, and beet greens are excellent choices for increasing your potassium intake, as highlighted by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. These vegetables can be prepared in various ways to suit your taste preferences.
- Sweet Potatoes: A medium-sized sweet potato, baked with the skin on, contains about 542 mg of potassium.
- Spinach: One cup of cooked spinach provides approximately 839 mg of potassium and is also rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Beet Greens: Cooked beet greens offer around 1309 mg of potassium per cup, making them one of the most potassium-rich vegetables.
- Potatoes: A medium-sized baked potato with the skin on contains about 926 mg of potassium.
2.3. Legumes and Beans for Potassium
Which legumes and beans are high in potassium? White beans, kidney beans, and lentils are excellent plant-based sources of potassium, according to a report by the National Kidney Foundation. These can be incorporated into soups, stews, and salads for a nutritious meal.
- White Beans: One cup of cooked white beans contains approximately 1189 mg of potassium, making them an exceptional source.
- Kidney Beans: Cooked kidney beans provide about 713 mg of potassium per cup and are also a good source of protein and fiber.
- Lentils: One cup of cooked lentils contains around 731 mg of potassium and is a versatile ingredient for various dishes.
2.4. Dairy Products with Potassium
Do dairy products contribute to potassium intake? Yes, dairy products like milk and yogurt are good sources of potassium, as confirmed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. These can be easily incorporated into your daily diet.
- Milk: One cup of milk contains about 350-380 mg of potassium, depending on the type (e.g., whole, skim).
- Yogurt: A cup of plain yogurt provides approximately 450-500 mg of potassium and is also a good source of probiotics.
3. Delicious Recipes Featuring High-Potassium Foods
Looking for ways to incorporate potassium-rich foods into your meals? Here are some delicious recipes featuring high-potassium ingredients, perfect for cooking enthusiasts in the USA. These recipes are designed to be both nutritious and easy to prepare, making them ideal for incorporating into your daily diet.
From breakfast to dinner, these recipes offer a variety of options to increase your potassium intake while enjoying flavorful meals. Check out larosafoods.com for more exciting recipes and meal ideas.
3.1. Potassium-Packed Breakfast Ideas
What are some quick and healthy breakfast options with potassium-rich foods? Try a banana smoothie with spinach, a sweet potato and black bean breakfast burrito, or oatmeal with sliced kiwis, as suggested by registered dietitians on larosafoods.com. These breakfasts are not only delicious but also provide a significant potassium boost to start your day.
- Banana Smoothie with Spinach: Blend one banana, a handful of spinach, almond milk, and a scoop of protein powder for a quick and nutritious smoothie.
- Sweet Potato and Black Bean Breakfast Burrito: Sauté diced sweet potato with black beans, onions, and peppers. Wrap in a whole-wheat tortilla for a hearty breakfast.
- Oatmeal with Sliced Kiwis: Prepare oatmeal according to package instructions and top with sliced kiwis, a sprinkle of nuts, and a drizzle of honey.
3.2. Lunch Recipes with Potassium
What are some satisfying lunch recipes that include high-potassium foods? Consider a spinach and white bean salad, a sweet potato and lentil soup, or an avocado and turkey wrap, recommended by nutrition experts on larosafoods.com. These lunches are both filling and packed with potassium.
- Spinach and White Bean Salad: Combine fresh spinach, cooked white beans, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and a lemon vinaigrette dressing.
- Sweet Potato and Lentil Soup: Simmer diced sweet potato with lentils, carrots, celery, and vegetable broth. Season with herbs and spices to taste.
- Avocado and Turkey Wrap: Spread mashed avocado on a whole-wheat tortilla, add sliced turkey breast, spinach, and a sprinkle of red pepper flakes.
3.3. Dinner Ideas Rich in Potassium
What are some dinner recipes that feature potassium-rich ingredients? Try baked cod with roasted sweet potatoes and spinach, kidney bean chili, or grilled chicken with a side of steamed beet greens, inspired by culinary creations on larosafoods.com. These dinners offer a delicious way to meet your potassium needs.
- Baked Cod with Roasted Sweet Potatoes and Spinach: Season cod fillets with herbs and spices and bake until flaky. Roast diced sweet potatoes and sauté spinach with garlic and olive oil.
- Kidney Bean Chili: Combine cooked kidney beans with diced tomatoes, onions, peppers, corn, and chili seasoning. Simmer until flavors meld.
- Grilled Chicken with Steamed Beet Greens: Grill chicken breast until cooked through. Steam beet greens until tender and season with lemon juice and olive oil.
3.4. Snack Options to Boost Potassium
What are some convenient snack options that can help increase your potassium intake? Opt for a banana with almond butter, dried apricots, or a small yogurt parfait, as suggested by health-conscious foodies on larosafoods.com. These snacks are easy to prepare and perfect for a quick potassium boost.
- Banana with Almond Butter: Spread a tablespoon of almond butter on a banana for a satisfying and potassium-rich snack.
- Dried Apricots: A handful of dried apricots provides a concentrated source of potassium and is easy to take on the go.
- Yogurt Parfait: Layer yogurt with granola and sliced fruits like bananas or kiwis for a delicious and nutritious parfait.
4. Who Needs to Pay Attention to Potassium Intake?
Who should be particularly mindful of their potassium intake? People with kidney disease, those taking diuretics, and individuals with high blood pressure need to monitor their potassium levels closely, according to the National Kidney Foundation. It’s important to maintain a balanced intake to avoid complications.
These individuals may need to work with healthcare professionals and registered dietitians to manage their potassium intake effectively. Regular monitoring and dietary adjustments can help prevent imbalances and support overall health.
4.1. Individuals with Kidney Disease
Why do people with kidney disease need to be careful about potassium intake? Damaged kidneys may not effectively regulate potassium levels, leading to hyperkalemia (high potassium) or hypokalemia (low potassium), as explained by the American Kidney Fund. Careful dietary management is crucial for these individuals.
- Hyperkalemia: In individuals with kidney disease, the kidneys may not be able to remove excess potassium from the blood, leading to high potassium levels. This can cause serious heart problems and requires careful management.
- Hypokalemia: Some kidney conditions and certain medications can cause the kidneys to lose too much potassium, leading to low potassium levels. This can cause muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart arrhythmias.
4.2. People Taking Diuretics
How do diuretics affect potassium levels? Certain diuretics can cause potassium loss through increased urination, potentially leading to hypokalemia, according to the Mayo Clinic. Monitoring potassium levels and adjusting the diet accordingly is important for these individuals.
- Potassium-Wasting Diuretics: These diuretics increase the excretion of potassium in the urine, which can lead to low potassium levels. Common examples include furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide.
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretics: These diuretics help the body retain potassium, which can be beneficial for individuals at risk of hypokalemia. Examples include spironolactone and amiloride.
4.3. Those with High Blood Pressure
Why is potassium important for individuals with high blood pressure? Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body, which can lower blood pressure, as reported by the American Heart Association. Including potassium-rich foods in the diet can be a natural way to manage hypertension.
- Sodium-Potassium Balance: Potassium helps to counteract the effects of sodium on blood pressure. By increasing potassium intake and reducing sodium intake, individuals with high blood pressure can often achieve better blood pressure control.
- Dietary Approaches: The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet emphasizes potassium-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products, to help lower blood pressure.
5. Risks of Potassium Deficiency and Excess
What are the potential health risks associated with potassium deficiency and excess? Potassium deficiency (hypokalemia) can lead to muscle weakness, heart arrhythmias, and fatigue, while potassium excess (hyperkalemia) can cause heart problems and muscle paralysis, according to the National Institutes of Health. Maintaining a balanced potassium level is crucial.
It’s important to recognize the symptoms of both conditions and seek medical attention if you suspect a potassium imbalance. Regular blood tests can help monitor potassium levels, especially for individuals at risk.
5.1. Symptoms of Potassium Deficiency (Hypokalemia)
What are the signs of potassium deficiency? Symptoms of hypokalemia include muscle weakness, fatigue, constipation, heart palpitations, and muscle cramps, as noted by the Mayo Clinic. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
- Muscle Weakness: Low potassium levels can affect muscle function, leading to weakness and difficulty with movement.
- Fatigue: Hypokalemia can cause persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Constipation: Potassium is important for digestive function, and low levels can lead to constipation.
- Heart Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats or palpitations can occur due to the impact of potassium on heart muscle function.
- Muscle Cramps: Low potassium can cause painful muscle cramps, especially in the legs.
5.2. Risks of Potassium Excess (Hyperkalemia)
What are the dangers of having too much potassium in the body? Hyperkalemia can cause heart arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and potentially life-threatening cardiac arrest, according to the American Heart Association. It’s important to manage potassium intake, especially for those with kidney issues.
- Heart Arrhythmias: High potassium levels can disrupt the normal electrical activity of the heart, leading to irregular heartbeats.
- Muscle Weakness: Although potassium is needed for muscle function, excessive levels can paradoxically cause muscle weakness.
- Cardiac Arrest: In severe cases, hyperkalemia can lead to cardiac arrest, a life-threatening condition in which the heart stops beating.
6. How to Monitor Your Potassium Intake
What are the best ways to monitor your potassium intake and ensure you’re getting the right amount? Keep a food diary, read nutrition labels, and consult with a registered dietitian, as recommended by nutrition experts on larosafoods.com. These steps can help you maintain a balanced diet and manage your potassium levels effectively.
Regular monitoring can help you make informed food choices and adjust your diet as needed to meet your individual potassium requirements.
6.1. Keeping a Food Diary
How can a food diary help you track your potassium intake? A food diary helps you record everything you eat and drink, making it easier to identify sources of potassium and ensure you’re meeting your daily requirements, as suggested by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
- Detailed Recording: Record the types and amounts of food you consume each day.
- Nutrient Analysis: Use a nutrition database or app to calculate the potassium content of your meals.
- Identifying Patterns: Look for patterns in your diet to see if you are consistently consuming enough potassium-rich foods.
6.2. Reading Nutrition Labels
Why is it important to read nutrition labels for potassium content? Nutrition labels provide valuable information about the potassium content of packaged foods, helping you make informed choices and track your intake, according to the FDA.
- Potassium Listing: Check the nutrition facts panel for the amount of potassium per serving.
- Percent Daily Value: Note the percent daily value (%DV) for potassium to see how much a serving contributes to your daily needs.
- Comparing Products: Compare labels to choose products that are higher in potassium and lower in sodium.
6.3. Consulting with a Registered Dietitian
When should you consult with a registered dietitian about your potassium intake? If you have kidney disease, are taking diuretics, or have concerns about your potassium levels, a registered dietitian can provide personalized advice and help you create a balanced meal plan, as recommended by the National Kidney Foundation.
- Personalized Recommendations: A dietitian can assess your individual needs and provide tailored recommendations based on your health status and dietary preferences.
- Meal Planning: They can help you create a meal plan that includes potassium-rich foods while avoiding foods that may exacerbate potassium imbalances.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: A dietitian can monitor your progress and make adjustments to your meal plan as needed to ensure you are meeting your potassium requirements safely and effectively.
7. Potassium-Rich Foods for Specific Dietary Needs
Looking for potassium-rich options that fit specific dietary needs? Whether you’re vegetarian, vegan, or gluten-free, there are plenty of ways to incorporate potassium into your diet, as explored by dietitians on larosafoods.com.
These dietary adaptations ensure that everyone can enjoy the benefits of potassium-rich foods, regardless of their dietary restrictions.
7.1. Vegetarian Sources of Potassium
What are the best vegetarian sources of potassium? Leafy greens, sweet potatoes, bananas, beans, and avocados are excellent vegetarian options for increasing your potassium intake, as recommended by the Vegetarian Resource Group.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with potassium and can be used in salads, smoothies, and cooked dishes.
- Sweet Potatoes: These versatile vegetables can be baked, roasted, or mashed and provide a good source of potassium.
- Bananas: A convenient and portable snack, bananas are a well-known source of potassium.
- Beans: Kidney beans, white beans, and lentils are excellent sources of potassium and can be used in soups, stews, and salads.
- Avocados: These creamy fruits are rich in potassium and healthy fats and can be used in salads, sandwiches, and dips.
7.2. Vegan Potassium Sources
What are some plant-based sources of potassium suitable for vegans? Tofu, edamame, coconut water, and dried fruits are great vegan options for boosting your potassium intake, as highlighted by the Vegan Society.
- Tofu: This versatile soy product can be used in stir-fries, scrambles, and baked dishes and is a good source of potassium.
- Edamame: These young soybeans can be steamed or boiled and provide a delicious and nutritious source of potassium.
- Coconut Water: This refreshing beverage is a natural source of electrolytes, including potassium.
- Dried Fruits: Apricots, raisins, and prunes are concentrated sources of potassium and can be used in snacks and baked goods.
7.3. Gluten-Free Potassium-Rich Foods
What gluten-free foods are high in potassium? Potatoes, sweet potatoes, spinach, bananas, and oranges are naturally gluten-free and rich in potassium, making them excellent choices for those with gluten sensitivities, as suggested by the Celiac Disease Foundation.
- Potatoes: Both white and sweet potatoes are gluten-free and provide a good source of potassium.
- Spinach: This leafy green is naturally gluten-free and can be used in a variety of dishes.
- Bananas: These fruits are naturally gluten-free and provide a convenient source of potassium.
- Oranges: These citrus fruits are gluten-free and offer a refreshing source of potassium and vitamin C.
8. Expert Tips for Maximizing Potassium Intake
How can you maximize your potassium intake through your diet? Steam or bake vegetables to retain potassium, avoid over-processing foods, and pair potassium-rich foods with those that enhance absorption, as advised by culinary and nutrition experts on larosafoods.com. These tips can help you get the most out of the potassium in your diet.
Implementing these strategies can ensure that you’re not only consuming potassium-rich foods but also optimizing their nutritional benefits.
8.1. Best Cooking Methods to Retain Potassium
What are the best cooking methods to preserve potassium in foods? Steaming, baking, and grilling are preferable to boiling, which can leach potassium into the water, according to a study in the Journal of Food Science.
- Steaming: This method helps retain nutrients by cooking foods gently with steam, minimizing nutrient loss.
- Baking: Baking at moderate temperatures helps preserve potassium and other nutrients in foods.
- Grilling: Grilling can help retain potassium while adding flavor, but be careful not to overcook foods, which can reduce nutrient content.
8.2. Foods That Enhance Potassium Absorption
Which foods can help enhance potassium absorption? Consuming potassium-rich foods with sources of vitamin D and magnesium can improve absorption, according to research from the University of California, Berkeley, in July 2025. For example, pair spinach with almonds and fortified dairy.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D helps the body absorb potassium more efficiently. Good sources of vitamin D include fortified dairy products, fatty fish, and sunlight exposure.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is essential for potassium transport and balance within the body. Good sources of magnesium include nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy greens.
8.3. Avoiding Processed Foods
Why is it important to limit processed foods when trying to increase potassium intake? Processed foods are often low in potassium and high in sodium, which can disrupt the sodium-potassium balance in the body, as noted by the American Heart Association.
- Sodium Content: Processed foods often contain high levels of sodium, which can counteract the benefits of potassium in regulating blood pressure.
- Nutrient Depletion: Processing can strip foods of their natural potassium content, reducing their nutritional value.
- Healthier Choices: Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible to maximize your potassium intake and overall health.
9. Addressing Common Myths About Potassium
What are some common misconceptions about potassium? One myth is that bananas are the only good source of potassium, while another is that you can easily get enough potassium from supplements alone, as clarified by nutrition experts on larosafoods.com. It’s important to have accurate information to make informed dietary choices.
Debunking these myths can help individuals focus on a balanced and varied diet to meet their potassium needs effectively.
9.1. Bananas Are the Only Source of Potassium
Is it true that bananas are the only significant source of potassium? While bananas are a good source, many other foods, such as sweet potatoes, spinach, and beans, offer even higher amounts of potassium, according to the USDA National Nutrient Database.
- Variety of Sources: Emphasize the importance of including a variety of potassium-rich foods in the diet, rather than relying solely on bananas.
- Nutrient Diversity: Other foods offer additional nutrients that bananas may not provide, contributing to a more balanced and nutritious diet.
9.2. Potassium Supplements Are Sufficient
Can you rely solely on supplements to meet your potassium needs? While potassium supplements can be helpful in certain situations, they should not replace a balanced diet, as they can lead to potassium toxicity if not taken correctly, as advised by the Mayo Clinic.
- Dietary Priority: Focus on obtaining potassium from whole foods whenever possible, as they provide a variety of nutrients and are less likely to cause potassium imbalances.
- Supplement Use: Use potassium supplements only under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use.
10. Potassium and Exercise: What You Need to Know
How does potassium affect exercise performance and recovery? Potassium is crucial for muscle function and electrolyte balance, helping prevent cramps and improve endurance during physical activity, according to sports nutrition experts on larosafoods.com.
Understanding the role of potassium in exercise can help athletes and fitness enthusiasts optimize their performance and recovery through proper nutrition.
10.1. Potassium’s Role in Muscle Function During Exercise
Why is potassium important for muscle function during exercise? Potassium helps regulate muscle contractions and nerve impulses, ensuring muscles function efficiently during physical activity, according to a study in the Journal of Applied Physiology.
- Muscle Contractions: Potassium plays a key role in the electrical activity of muscle cells, enabling them to contract and relax properly.
- Nerve Impulses: Potassium is essential for transmitting nerve signals that control muscle movements.
- Preventing Cramps: Adequate potassium levels can help prevent muscle cramps and spasms during exercise.
10.2. Electrolyte Balance and Hydration
How does potassium contribute to electrolyte balance and hydration during exercise? Potassium is an important electrolyte that helps maintain fluid balance and prevent dehydration, which is crucial for optimal performance, as noted by the American College of Sports Medicine.
- Fluid Balance: Potassium helps regulate the movement of fluids between cells, ensuring proper hydration.
- Sweat Loss: Potassium is lost through sweat during exercise, so it’s important to replenish it to maintain electrolyte balance.
- Hydration Strategies: Consume potassium-rich foods and beverages, such as coconut water, to stay hydrated and maintain electrolyte balance during exercise.
10.3. Post-Exercise Recovery
How can potassium aid in post-exercise recovery? Potassium helps restore muscle function, reduce inflammation, and replenish glycogen stores after exercise, supporting faster recovery, as suggested by sports nutritionists on larosafoods.com.
- Muscle Recovery: Potassium helps repair and rebuild muscle tissue after exercise.
- Inflammation Reduction: Potassium has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce muscle soreness and inflammation after exercise.
- Glycogen Replenishment: Potassium helps transport glucose into muscle cells, replenishing glycogen stores and providing energy for future workouts.
Incorporating potassium-rich foods into your diet is essential for maintaining optimal health, especially for those who enjoy cooking and exploring new recipes. From fruits and vegetables to legumes and dairy products, there are plenty of delicious ways to boost your potassium intake. Whether you’re looking for breakfast ideas, lunch recipes, dinner options, or snack suggestions, larosafoods.com offers a wealth of resources to help you create balanced and nutritious meals.
Ready to explore the world of potassium-rich foods and enhance your culinary creations? Visit larosafoods.com today to discover a wide range of recipes, cooking tips, and nutritional information. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to improve your health and enjoy delicious, potassium-packed meals. Contact us at 1 S Park St, San Francisco, CA 94107, United States or call +1 (415) 987-0123 to learn more. Your journey to a healthier and tastier lifestyle starts now.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Potassium
1. What is the recommended daily intake of potassium?
The recommended daily intake of potassium is 3,500-4,700 mg for adults, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
2. Can low potassium cause muscle cramps?
Yes, low potassium levels (hypokalemia) can lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and spasms, as noted by the Mayo Clinic.
3. Are bananas the best source of potassium?
While bananas are a good source, many other foods, such as sweet potatoes, spinach, and beans, offer even higher amounts of potassium, according to the USDA National Nutrient Database.
4. Can too much potassium be harmful?
Yes, too much potassium (hyperkalemia) can cause heart arrhythmias, muscle weakness, and potentially life-threatening cardiac arrest, according to the American Heart Association.
5. How can I increase my potassium intake through diet?
Include potassium-rich foods such as bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, beans, and avocados in your daily meals, as suggested by registered dietitians on larosafoods.com.
6. What are the best cooking methods to retain potassium in foods?
Steaming, baking, and grilling are preferable to boiling, which can leach potassium into the water, according to a study in the Journal of Food Science.
7. Who should be careful about their potassium intake?
People with kidney disease, those taking diuretics, and individuals with high blood pressure need to monitor their potassium levels closely, according to the National Kidney Foundation.
8. Can potassium supplements replace potassium-rich foods?
While potassium supplements can be helpful in certain situations, they should not replace a balanced diet, as they can lead to potassium toxicity if not taken correctly, as advised by the Mayo Clinic.
9. How does potassium affect exercise performance?
Potassium is crucial for muscle function and electrolyte balance, helping prevent cramps and improve endurance during physical activity, according to sports nutrition experts on larosafoods.com.
10. What are some vegan sources of potassium?
Tofu, edamame, coconut water, and dried fruits are great vegan options for boosting your potassium intake, as highlighted by the Vegan Society.